"Nano-sized 'Brain' Network Learns and Remembers in Real Time"
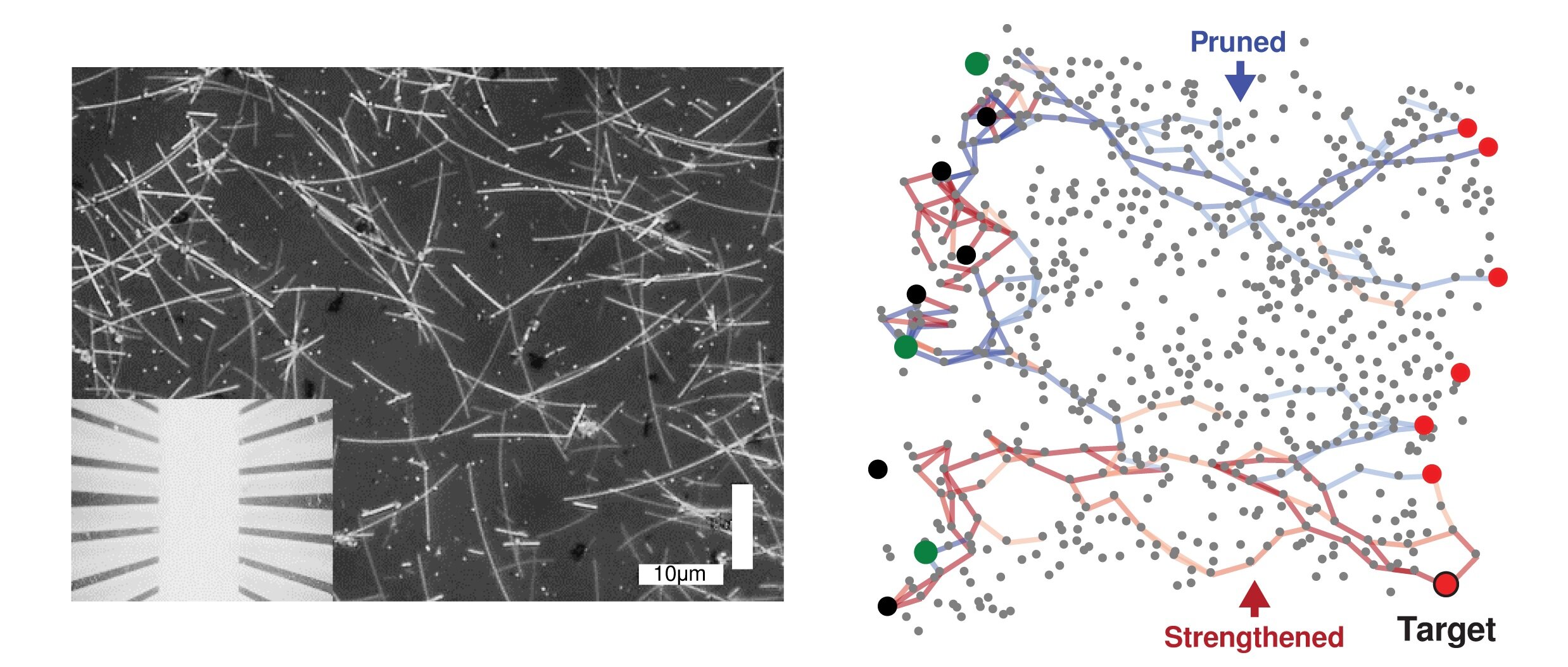
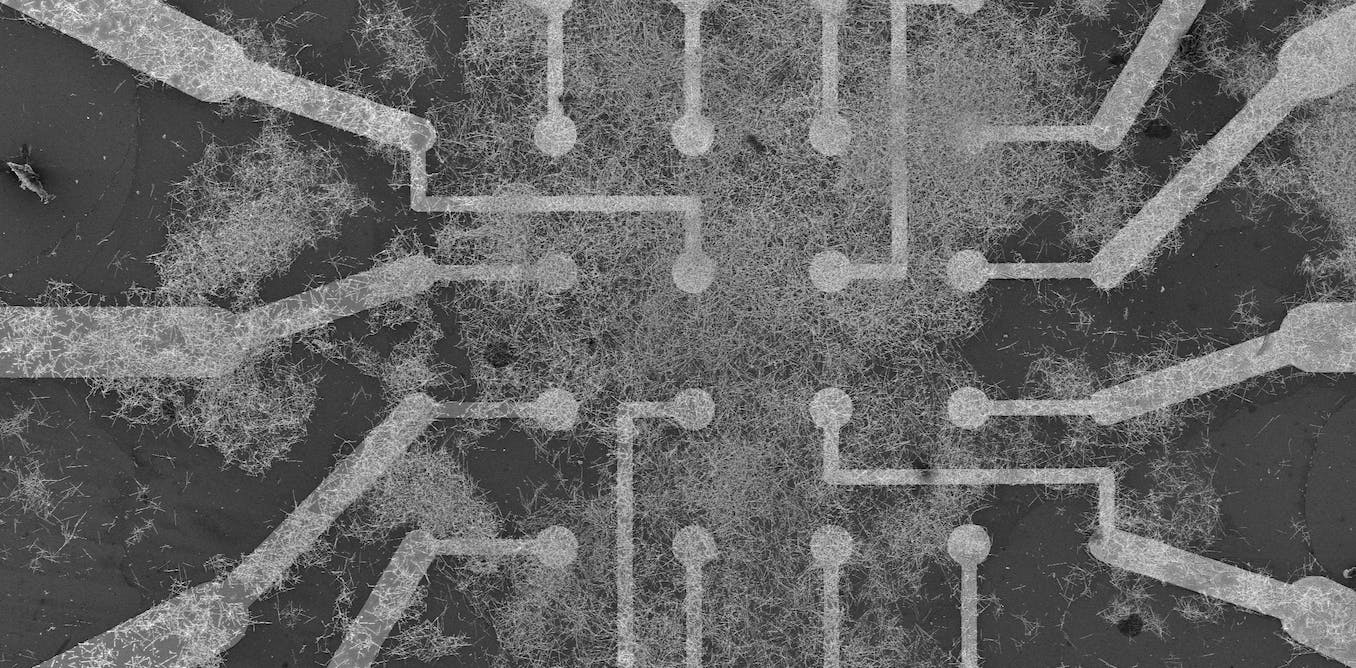
Researchers have developed a physical neural network using silver nanowires that can learn and adapt in real time, outperforming computer-based AI systems. The nanowire networks, resembling the structure of neurons in the brain, can efficiently process and transmit information through electrical signals. Unlike conventional batch-based learning, the network's online learning approach requires less memory and energy, making it more efficient. The network successfully recognized handwritten numbers and demonstrated the ability to remember patterns of digits, showcasing its potential for emulating brain-like learning and memory.