Wyoming reports influenza-related child death, urging vaccines
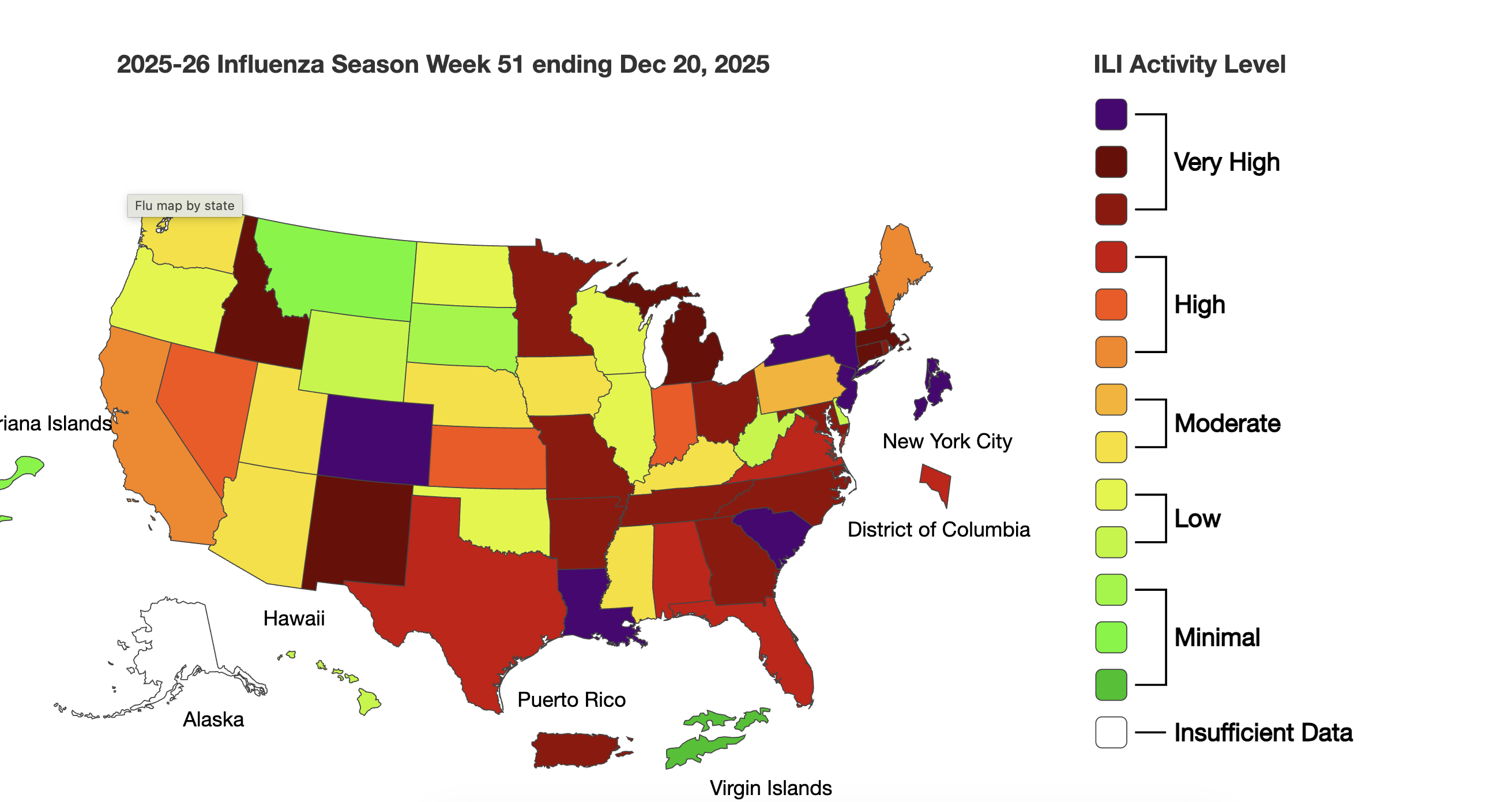
The Wyoming Department of Health announced the death of a Fremont County child from influenza, part of a season dominated by the H3N2 strain; officials say flu can be serious, encourage annual vaccination, and outline preventive measures and antiviral treatment, noting nationwide pediatric deaths and that most affected children were not up to date on vaccines.