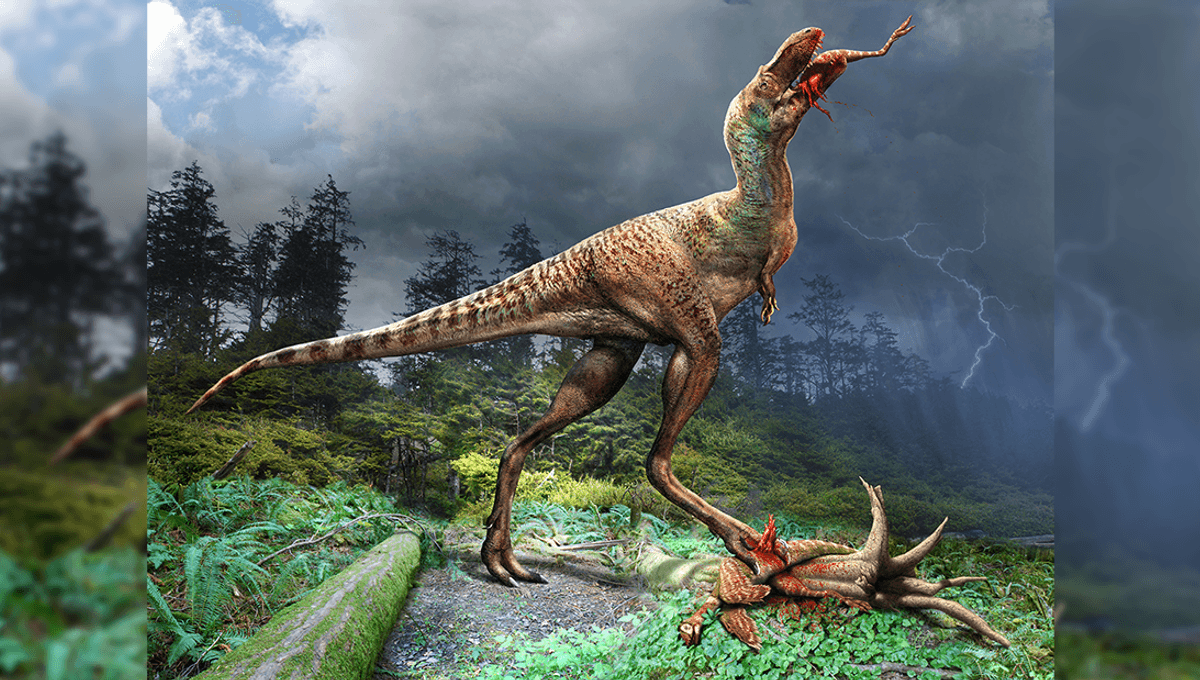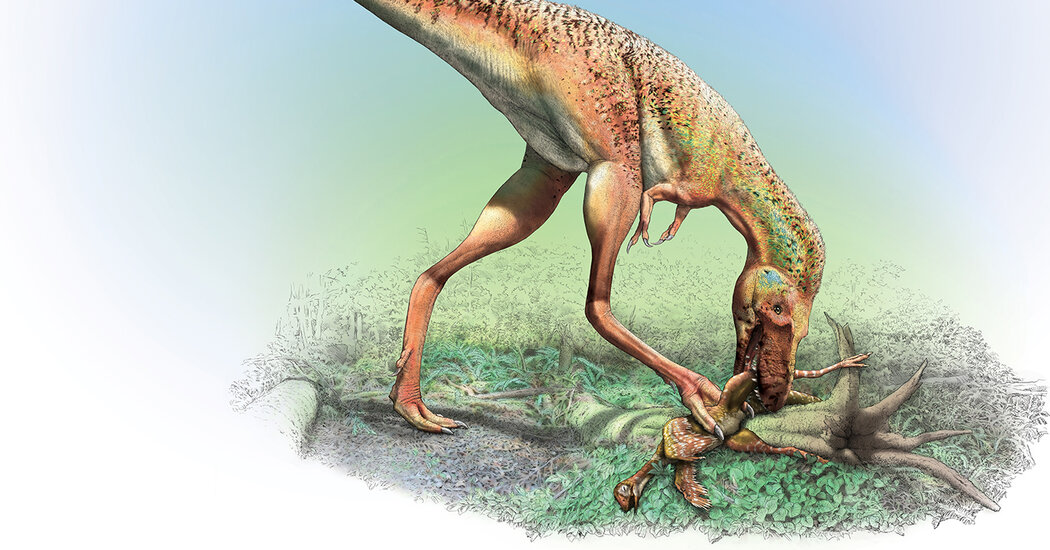
Teenage Tyrannosaur's Fossilized Stomach Unveils Prey Preference
The fossil of a 75-million-year-old Gorgosaurus, a relative of Tyrannosaurus rex, has been discovered with preserved stomach contents, providing insight into the feeding behavior of young tyrannosaurs. The fossil contains the hind limbs of two small feathered dinosaurs, indicating that young tyrannosaurs fed on different animals than their adult counterparts. This finding supports the theory that young tyrannosaurs were nimble predators, filling a midsize predator niche before maturing into apex predators. The fossil also suggests that Gorgosaurus could not take on large herbivores until the age of 11.