Unraveling the Genetic and Epidemiological Landscape of Clonal Hematopoiesis
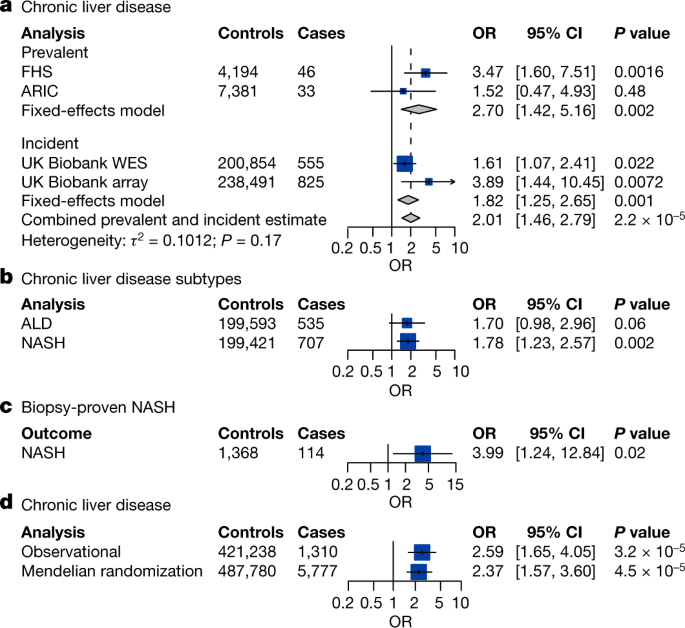
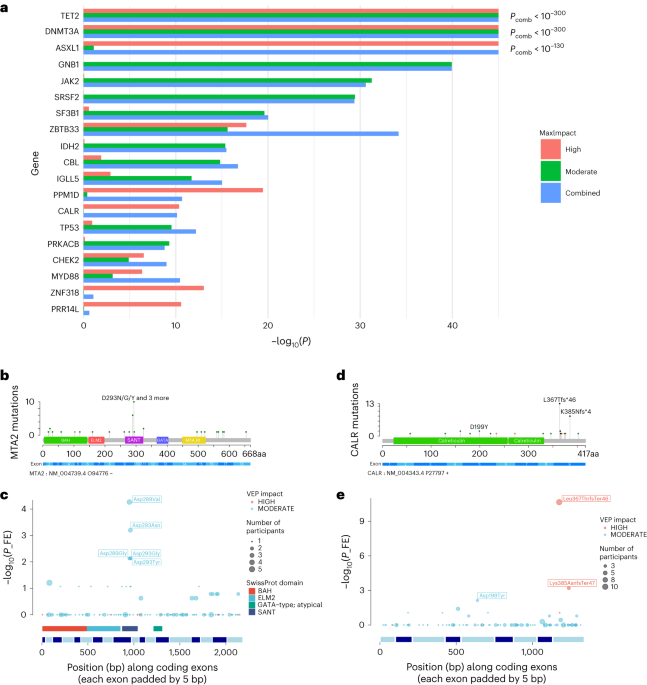
Clonal hematopoiesis (CH), the expansion of a few clones of hematopoietic stem cells, is associated with reduced life expectancy and increased risk of hematological neoplasia. A study using whole-genome sequencing of blood samples from over 176,000 participants identified 16,306 cases of CH, with a prevalence of 9.3%. CH was more common in older individuals and strongly associated with smoking. CH was also linked to increased risks of myeloid and lymphoid neoplasia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, peripheral artery disease, emphysema, and alcohol abuse. However, no significant association was found between CH and cardiovascular disease or inflammatory conditions. Genetic analysis revealed mutations in known myeloid disease genes, as well as novel associations with other genes. The study provides insights into the epidemiology and genetics of CH and its association with various diseases.