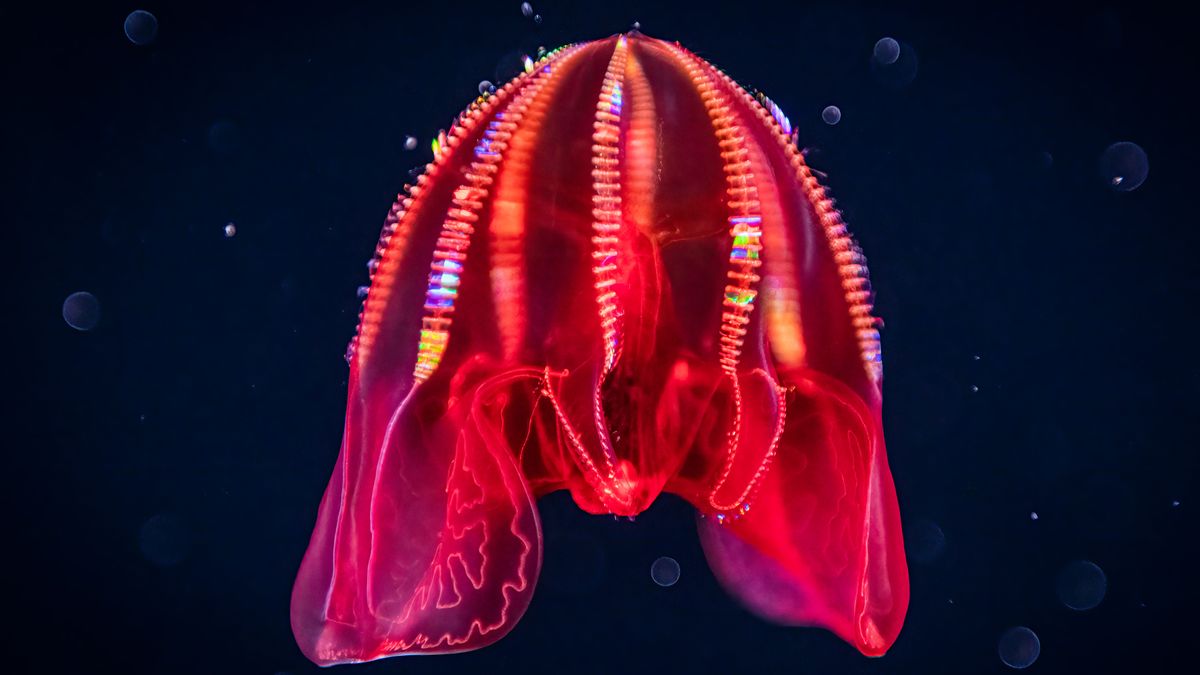
Scientists Discover First Branch in the Tree of Life
Scientists have identified the comb jelly as the first animal to branch off from the common ancestor of all animals, using new chromosomal analysis techniques that compare gene arrangements across species, resolving a long-standing debate between sponges and comb jellies.