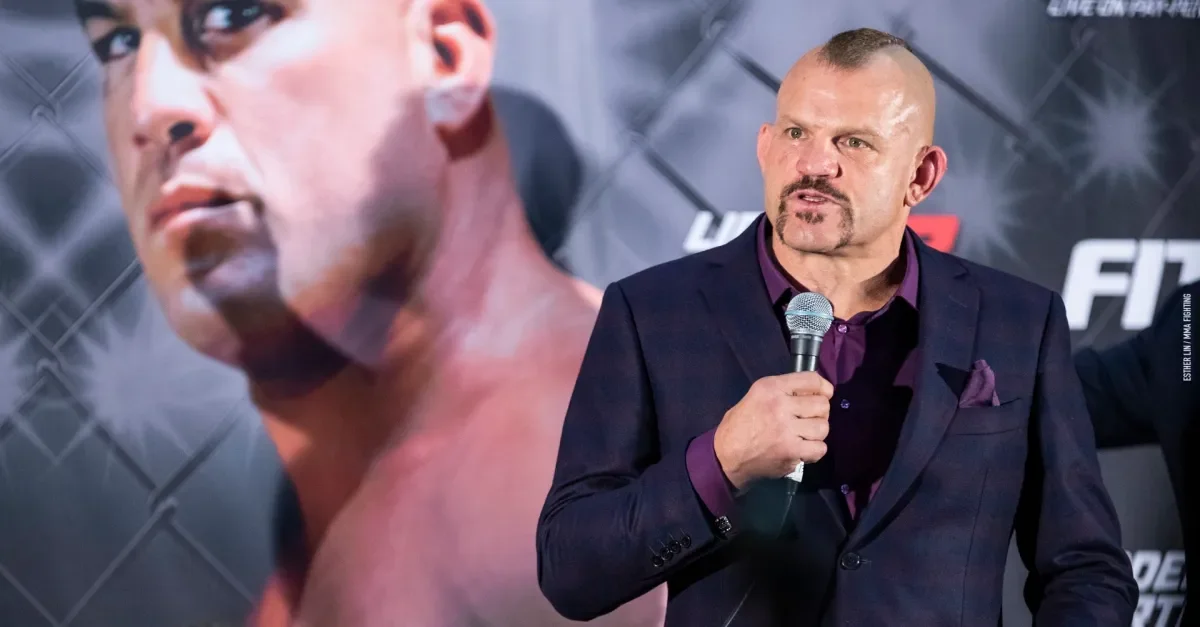
Liddell credits neck surgery and vocal-cord damage for changed voice, not brain injury
Chuck Liddell says his post-retirement speech changes are due to damaged vocal cords and a neck surgery after a 2018 bout, not a brain injury; he acknowledges mental challenges after fighting and notes that training provides a release and helps him cope with the aftereffects.