"Revolutionary Breakthrough: Antioxidant Enzymes Repair DNA Damage, Transforming Cellular Biology"
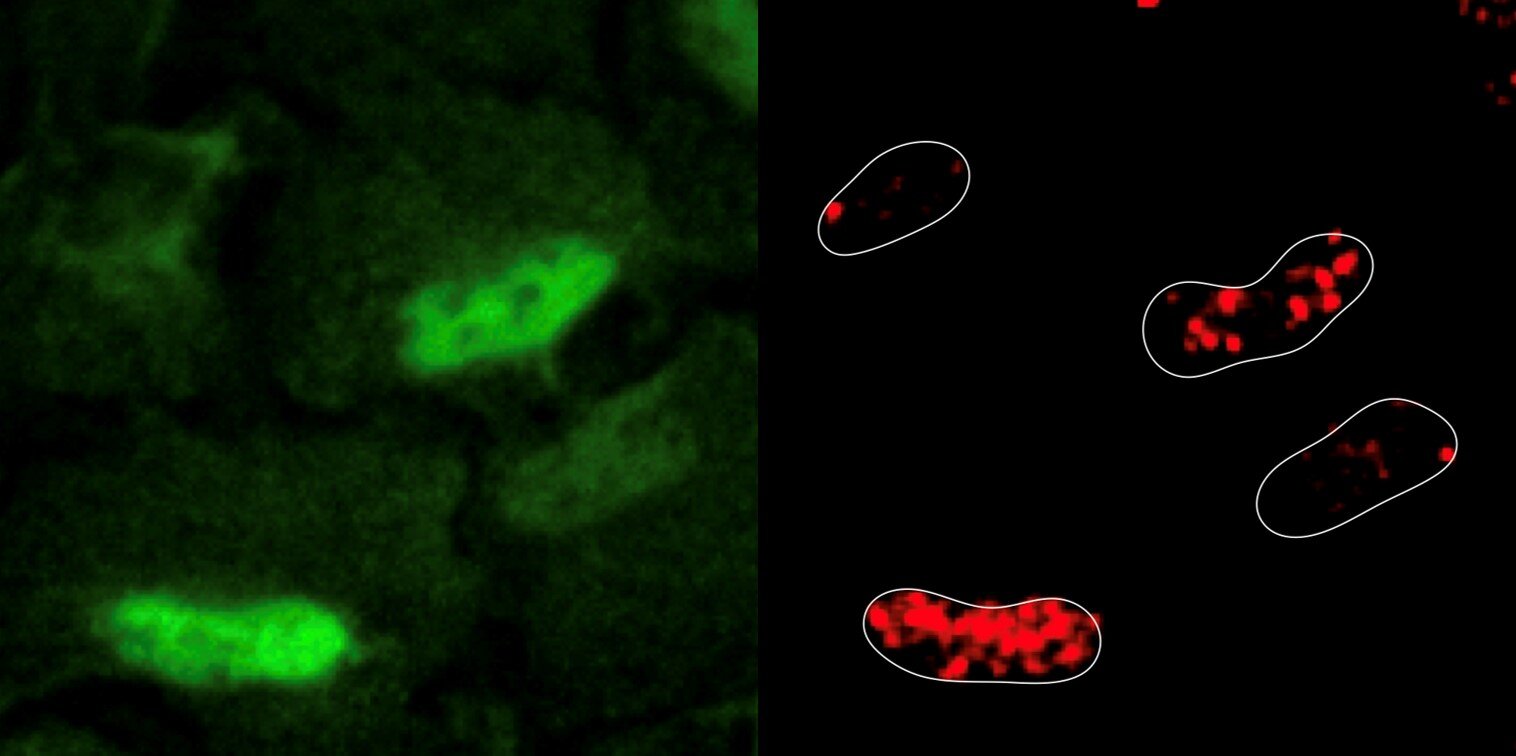
Researchers have made a profound paradigm shift in cellular biology by discovering that the cell nucleus is metabolically active and can protect DNA integrity by mobilizing antioxidant enzymes in response to DNA damage. This finding has significant implications for cancer research, as cancer cells often exploit metabolic processes for their growth. The study identified metabolic enzymes and processes essential for a cell's DNA damage response, revealing that reactive oxygen species accumulate in the nucleus during DNA damage. The enzyme PRDX1 was found to repair the damage and regulate the availability of aspartate, a critical raw material for DNA synthesis. The findings suggest new strategies for cancer treatment, such as combining chemotherapy drugs with agents that boost reactive oxygen species generation or inhibit nucleotide synthesis processes.