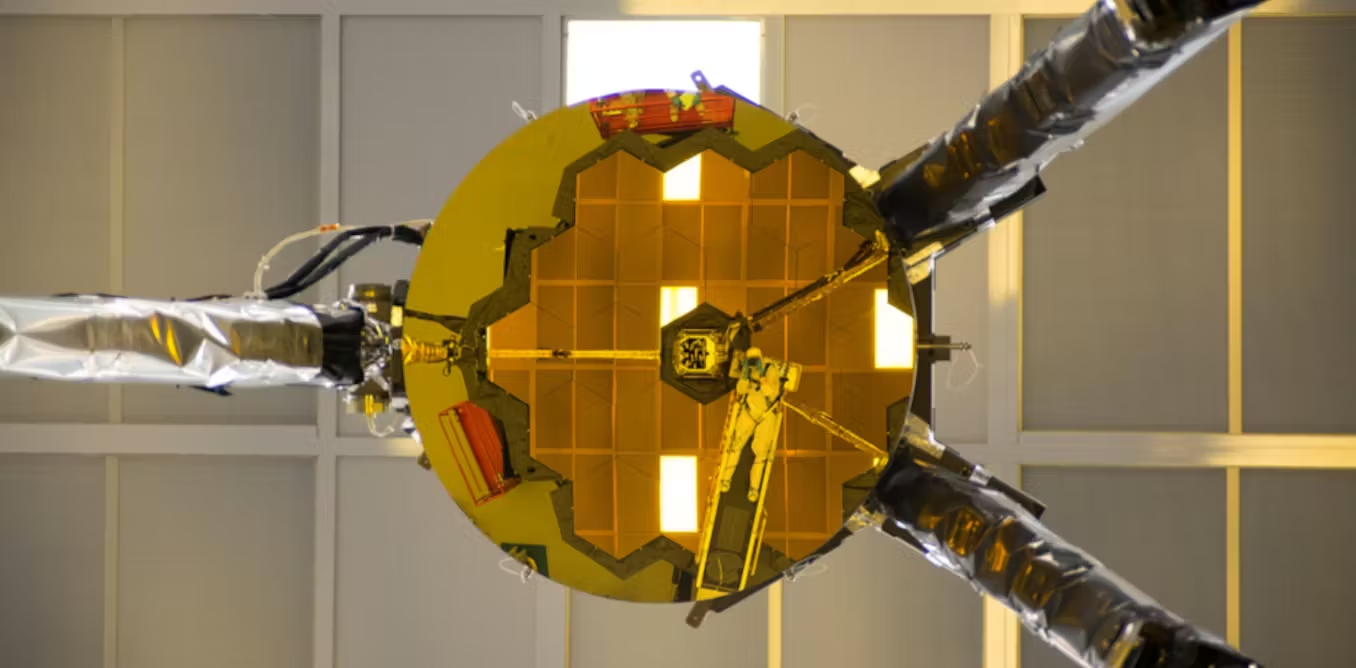
NASA uses AI to restore crystal-clear vision of James Webb Telescope
Scientists have enhanced the resolution of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope using a new technique called aperture masking interferometry (AMI), which corrects optical and electronic distortions in the telescope's images, enabling clearer observations of stars, planets, and black hole jets from a million miles away.