Evidence of Cannibalism Found on Ancient Human Relative's Bone
TL;DR Summary
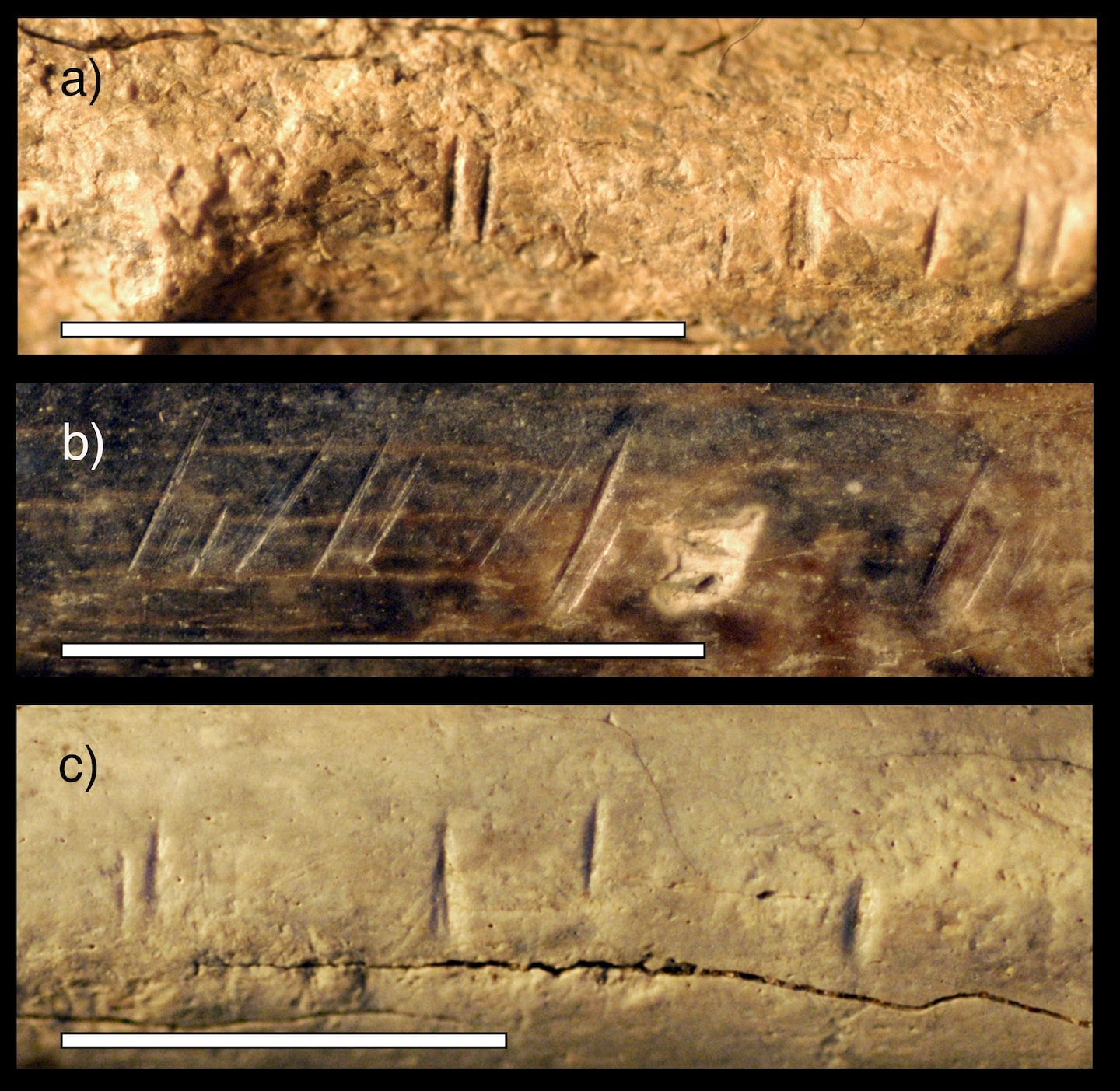
Cut marks made by a stone tool on a 1.5-million-year-old human relative's bone found in northern Kenya appear to be the oldest evidence of one hominin butchering another, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The discovery raises the possibility that the remains were cannibalized. Cannibalism requires that both the consumer and consumed be of the same species. The closer the practice gets to Homo sapiens, the more complex and uncomfortable the questions it raises.
- Signs of butchery, possible cannibalism found on ancient human relative's bone The Washington Post
- Hominids may have butchered one another about 1.45 million years ago Science News Magazine
- Humans' evolutionary relatives butchered one another 1.45 million years ago Phys.org
- Our Human Relatives Butchered and Ate Each Other 1.45 Million Years Ago Smithsonian Magazine
- Early Pleistocene cut marked hominin fossil from Koobi Fora, Kenya | Scientific Reports Nature.com
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
5 min
vs 6 min read
Condensed
92%
1,005 → 76 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on The Washington Post