Unveiling the Mechanism of Nucleosome Assembly and Histone Binding by Chromatin Assembly Factor-1
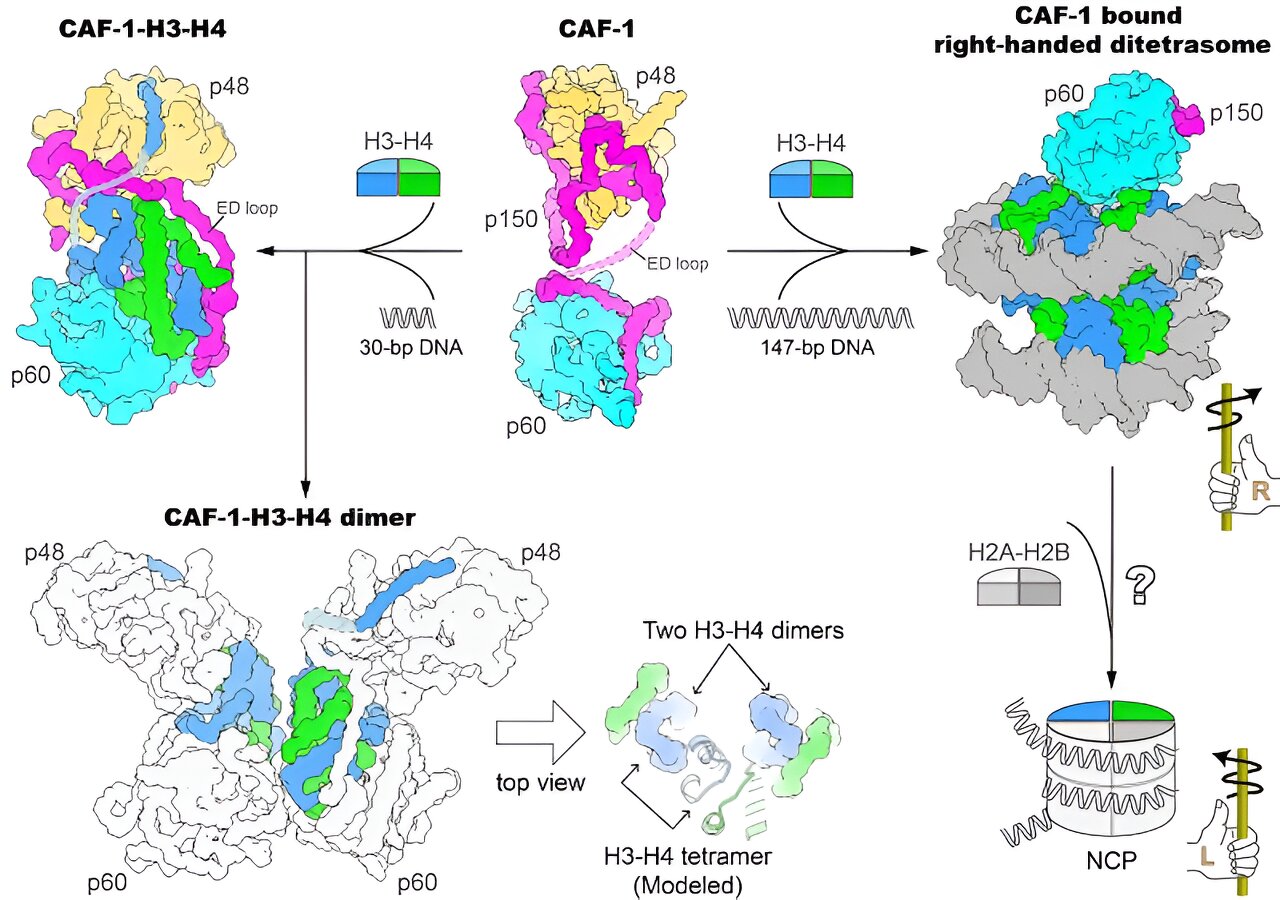
Researchers have revealed the mechanism of nucleosome assembly by chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1), a protein complex responsible for depositing newly synthesized histones onto DNA. Through high-resolution structures and cryo-EM imaging, they discovered that CAF-1 binds to histones H3-H4 through specific subunits and loops. They also found that a DNA oligomer triggers the dimerization of the CAF-1-H3-H4 complex, leading to the formation of an H3-H4 tetramer. Additionally, they observed a CAF-1-bound right-handed di-tetrasome structure, suggesting the involvement of a right-handed nucleosome precursor in replication-coupled nucleosome assembly. These findings provide insights into the molecular mechanism of de novo nucleosome assembly.
- Researchers unveil mechanism of nucleosome assembly by chromatin assembly factor-1 Phys.org
- FAP106 is an interaction hub for assembling microtubule inner proteins at the cilium inner junction Nature.com
- Structural insights into histone binding and nucleosome assembly by chromatin assembly factor-1 Science
- View Full Coverage on Google News
Reading Insights
0
5
2 min
vs 3 min read
81%
510 → 98 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org