Argonne supercomputer reveals crucial HIV protein mechanism for drug development.
TL;DR Summary
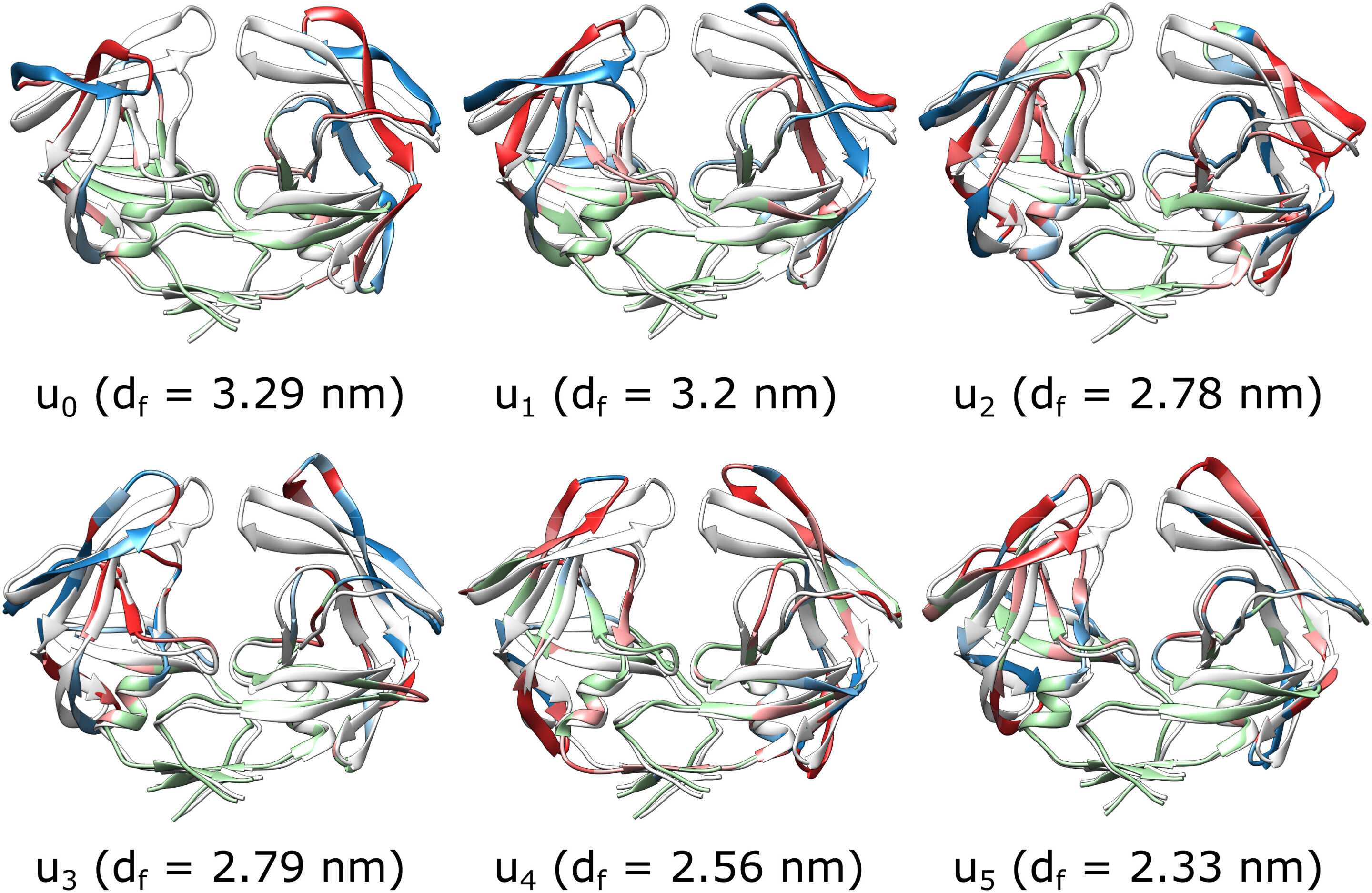
Researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have used the Theta supercomputer at the Argonne National Laboratory to identify the essential factors that control a certain structural change of HIV protease, a key viral protein. The structural change is called a flap opening, and it occurs when the virus is binding to another molecule, like an antiviral drug. Understanding this structure change is critical for drug development. The researchers identified six reaction coordinates that together completely determine how the protein's structure changes, which gives scientists a clear picture of how the flap opening occurs.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
2
Time Saved
3 min
vs 4 min read
Condensed
88%
766 → 94 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org