"Deep-Sea Sediments Reveal Global Warming's Impact on Ancient Ocean Anoxia"
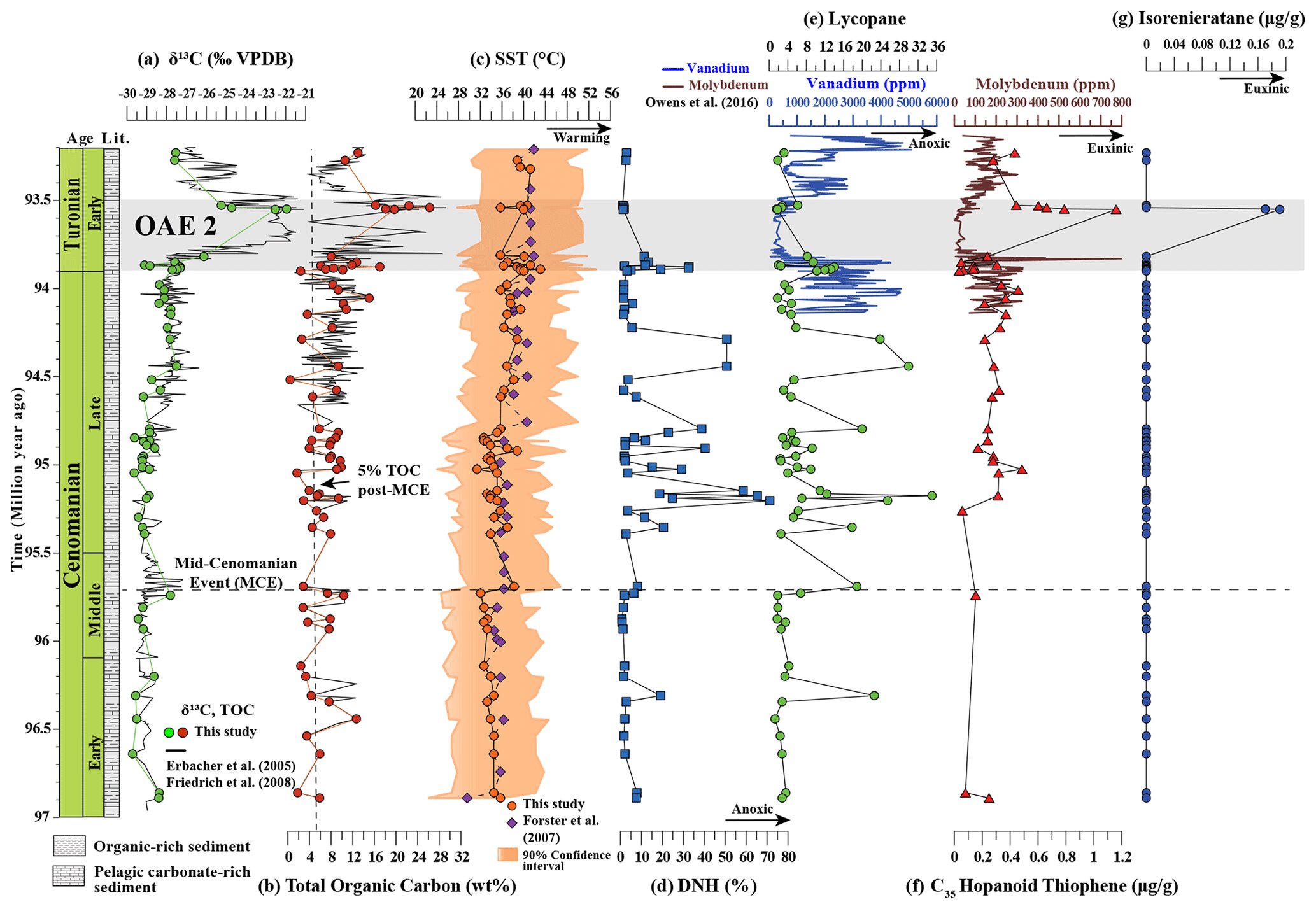
Research on deep-sea sediments from the Cenomanian period (~93.5 million years ago) suggests that Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE2) was caused by volcanic activity and climate warming, leading to widespread ocean anoxia. The study reveals a significant increase in total organic carbon content and sea surface temperature during this period, indicating a decline in oxygen levels. The findings highlight the potential future expansion of oxygen minimum zones in today's oceans due to global warming, posing a threat to marine ecosystems and biodiversity. Understanding past episodes of marine anoxia is crucial for guiding decisions to safeguard the future of Earth's oceans amidst ongoing climate change.
Reading Insights
0
2
6 min
vs 7 min read
93%
1,400 → 104 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org