Diverse autism mutations converge on a shared chromatin-regulation network in stem-cell–derived human cortex
TL;DR Summary
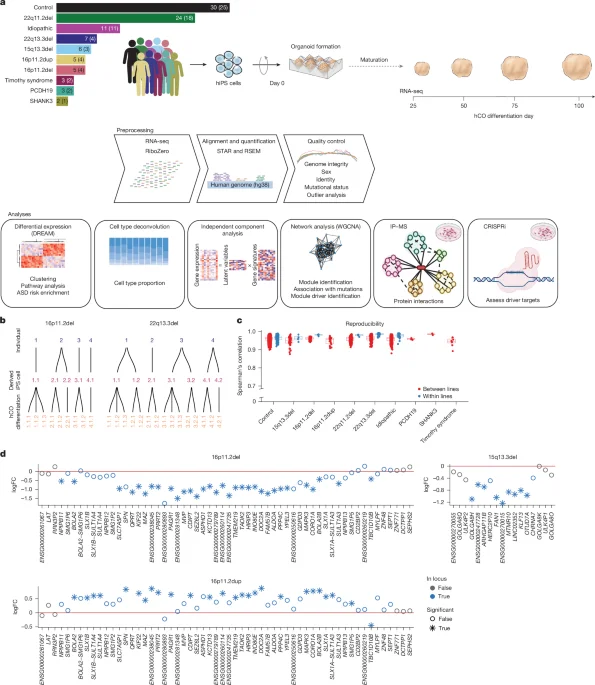
A large hiPSC-based study generated cortical organoids from eight ASD-risk mutations, idiopathic ASD, and controls, profiling gene expression across 25–100 days. Early mutation-specific changes give way to convergent transcriptional and chromatin-regulatory disruptions enriched for ASD risk genes, including SWI–SNF components. CRISPRi validation supports key regulators driving this convergent network, suggesting that diverse genetic risks in ASD propagate through shared transcriptional pathways that affect early neurodevelopment, while idiopathic cases show less convergence.
- Developmental convergence and divergence in human stem cell models of autism Nature
- Different Autism Mutations Can Lead to Similar Brain Changes Technology Networks
- Stem Cell Insights into Autism Development Patterns Bioengineer.org
- Brain Organoids Map How Distinct Autism Mutations Converge in Early Development GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
7
Time Saved
96 min
vs 97 min read
Condensed
100%
19,264 → 71 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature