Unveiling the Neural Circuitry Behind Maternal Response to Infant Cries
TL;DR Summary
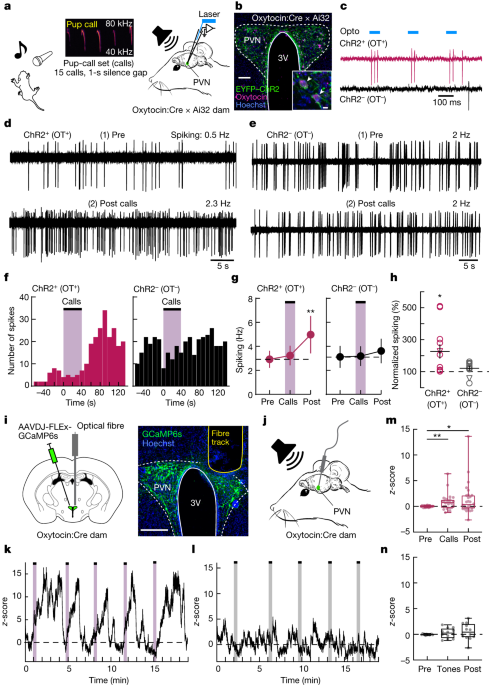
Researchers have identified the neural circuitry involved in the release of oxytocin, a hormone associated with maternal behavior, in response to infant cries. Using fiber photometry, the study found that specific populations of oxytocin neurons in the thalamus and hypothalamus are activated by infant vocalizations. The activation of these neurons promotes maternal behavior and bonding. This research provides insights into the neurobiology of maternal responses and may have implications for understanding postpartum anxiety and depression.
Topics:health#fiber-photometry#infant-cries#maternal-behavior#neural-circuitry#neuroscience#oxytocin
- Neural circuitry for maternal oxytocin release induced by infant cries Nature.com
- How Infant Cries Activate Mother's Nursing Response Neuroscience News
- The neural circuit that makes maternal mice respond to pups' cries Nature.com
- Newfound Brain Circuit Explains Why Infant Cries Prompt Milk Release NYU Langone Health
- Oxytocin Surge: Brain Circuit Discovered That Explains Why Infant Cries Prompt Milk Release SciTechDaily
- View Full Coverage on Google News
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
24 min
vs 25 min read
Condensed
98%
4,886 → 75 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com