"Dopamine's Role in Reinforcement Learning Unveiled"
TL;DR Summary
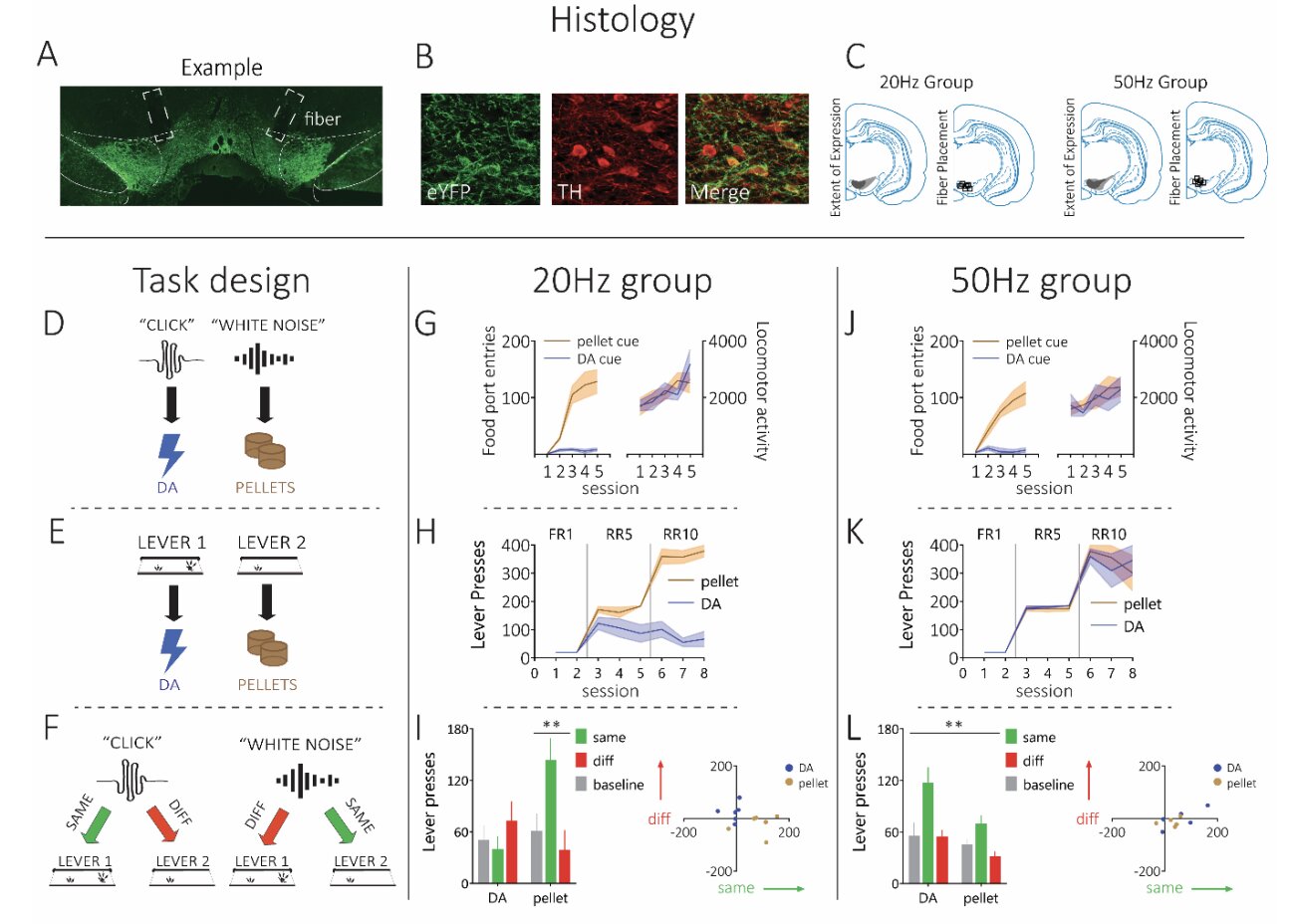
A study by researchers from UCLA, University of Sydney, and the State University of New Jersey reveals that dopamine neurons contribute to forming new mental associations between stimuli and rewards rather than attributing value to stimuli. High-frequency dopamine stimulation (50Hz) can function as a reward, while physiological frequency (20Hz) does not. This challenges the traditional view of dopamine as a neurotransmitter of pleasure and suggests its role in cognitive mapping and memory formation.
Topics:health#dopamine#intracranial-self-stimulation#neuroscience#pavlovian-conditioning#reinforcement-learning
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
5 min
vs 6 min read
Condensed
94%
1,141 → 73 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Medical Xpress