The Role of Sympathetic Nerves in T Cell Exhaustion and Suppression
TL;DR Summary
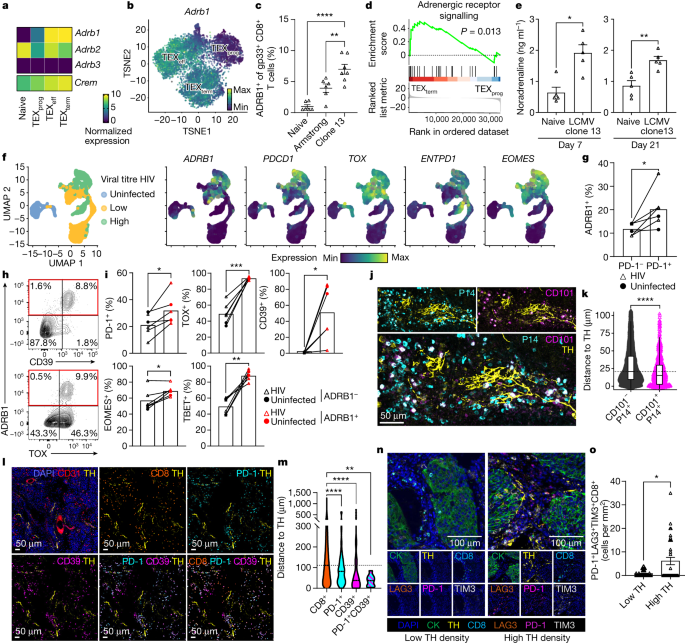
A new study has found that the β1-adrenergic receptor, which links sympathetic nerves to immune cells, plays a crucial role in T-cell exhaustion. T-cell exhaustion is a state of dysfunction that limits the immune response against cancer and chronic infections. The researchers discovered that blocking the β1-adrenergic receptor improved T-cell priming and enhanced the efficacy of cancer vaccines. This finding provides insights into the mechanisms of T-cell exhaustion and suggests potential therapeutic targets for improving immune responses in cancer immunotherapy.
Topics:health#b1-adrenergic-receptor#cancer-immunotherapy#immune-response#medical-research#sympathetic-nerves#t-cell-exhaustion
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
6
Time Saved
24 min
vs 25 min read
Condensed
98%
4,910 → 80 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com