Google Achieves Major Quantum Computing Breakthrough with Potential Bitcoin Impact
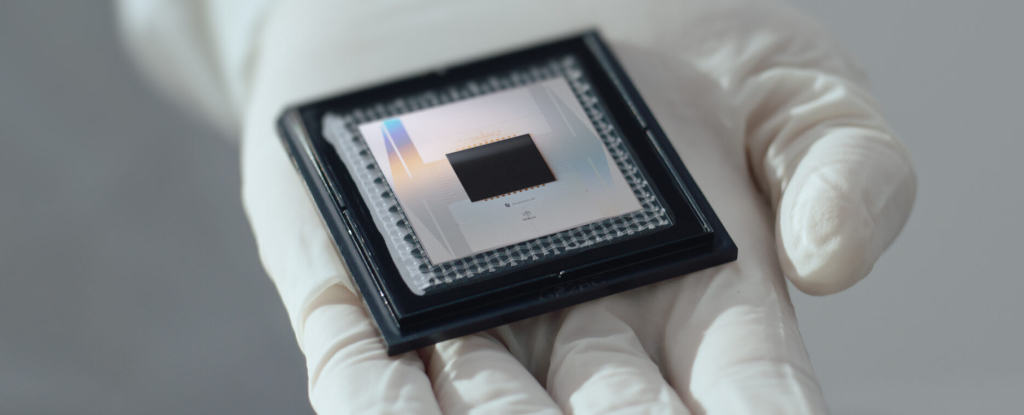
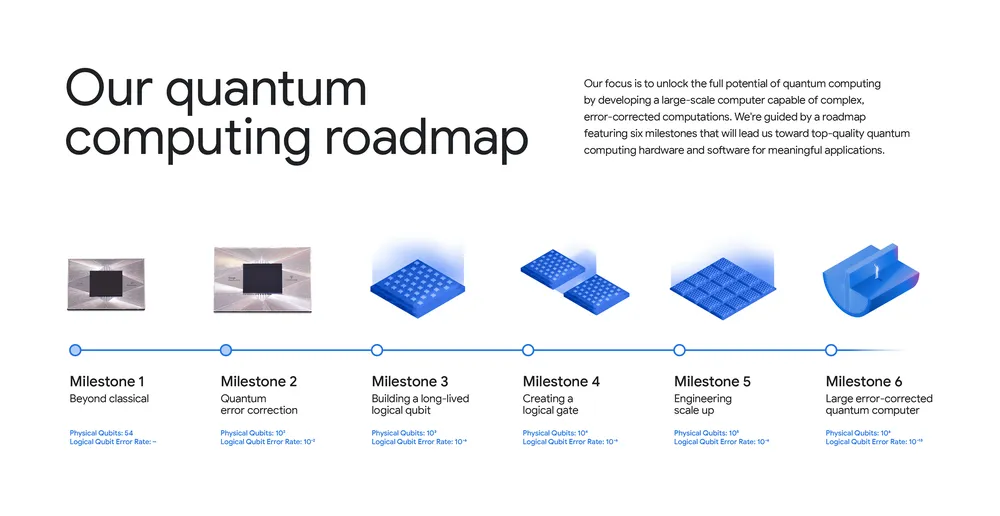
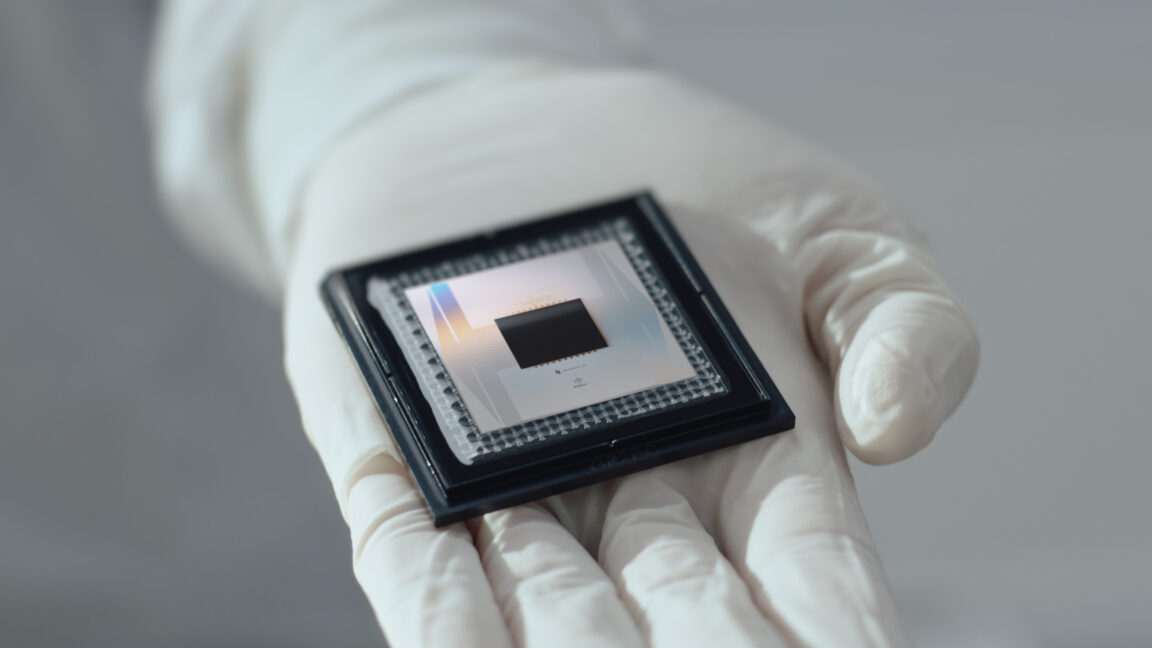
Google's CEO Sundar Pichai announced a major breakthrough in quantum computing with the Willow chip achieving the first verifiable quantum advantage, running algorithms 13,000 times faster than classical supercomputers, marking a significant step toward practical quantum applications and boosting Google's competitive edge in the field.