Astronomers Explore Supersoft X-ray Source Evolution
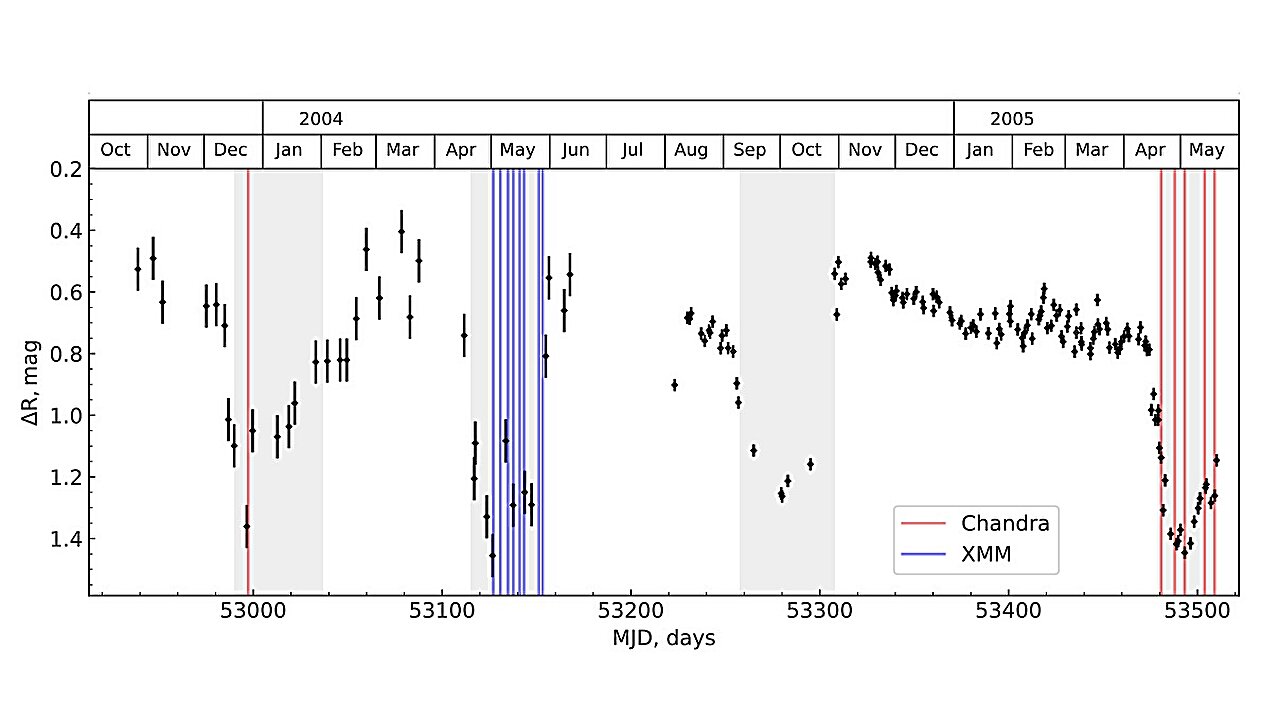
German astronomers have used ESA's XMM-Newton and NASA's Chandra to study the supersoft X-ray source RX J0513.9−6951, revealing insights into its evolution. The study found that the photospheric radius and bolometric luminosity of the white dwarf increase as optical flux decreases, challenging existing models. The researchers propose an alternative model where far ultraviolet/soft X-ray flux is reprocessed into the optical band due to scattering in a cloud system above the accretion disk, affecting the observed optical and X-ray states.
