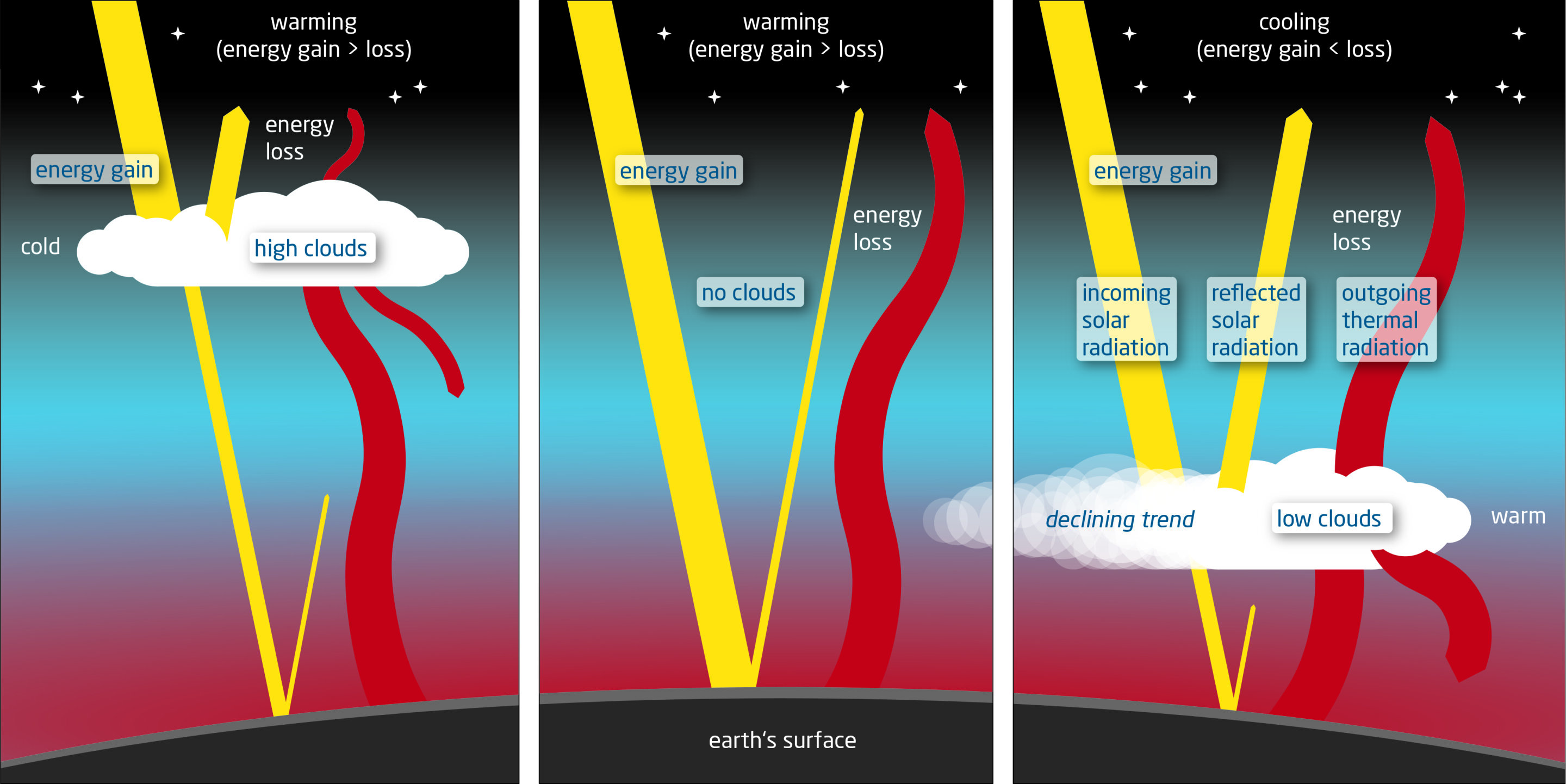
Diminished Cloud Cover and Albedo Linked to 2023's Record Heat
Researchers from the Alfred Wegener Institute have identified a decline in planetary albedo, particularly due to fewer low-altitude clouds, as a significant factor in the recent surge in global warming. This reduction in Earth's reflectivity has contributed to a 0.2 degrees Celsius increase in global temperatures, which was previously unexplained. The study suggests that this trend, exacerbated by reduced anthropogenic aerosols and natural fluctuations, could lead to more intense warming, potentially exceeding the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold sooner than anticipated.
