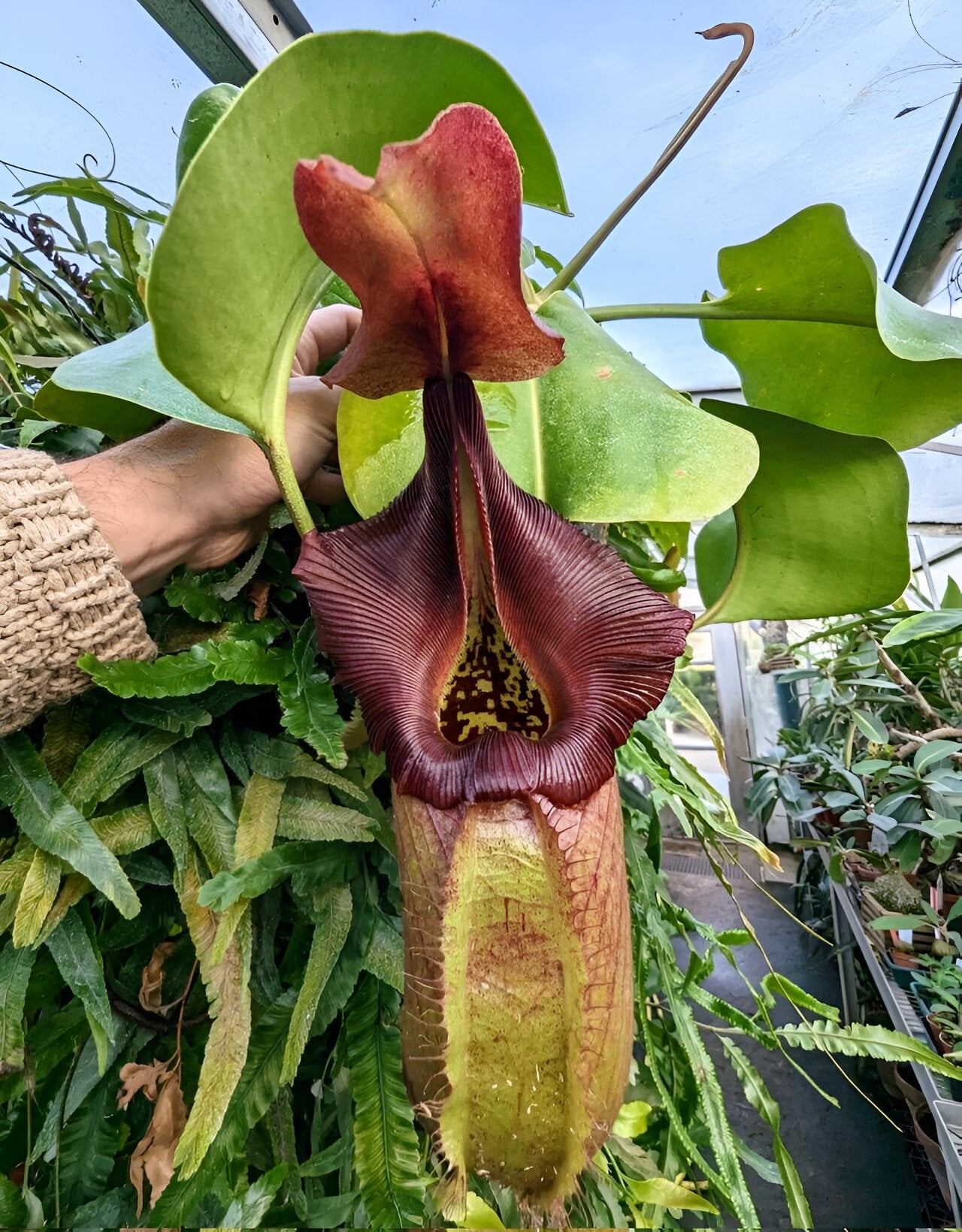
Decaploid pitcher plant genome uncovers subgenome dominance and novel gene evolution
Originally Published 2 years ago — by Nature.com
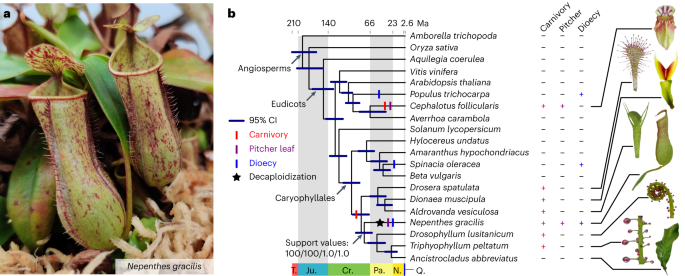
A study on the decaploid pitcher plant Nepenthes gracilis reveals that subgenome dominance plays a crucial role in shaping novel gene evolution. Polyploidy, the presence of multiple sets of chromosomes, has been linked to the diversification of angiosperms. The researchers found that one subgenome in Nepenthes gracilis exhibited higher expression levels and functional enrichment of genes involved in carnivory, while the other subgenome showed higher expression of genes related to flower development and sex determination. This subgenome dominance may have contributed to the adaptation and evolution of the pitcher plant's unique traits.

