Unlocking the Potential of Blood Stem Cells from Your Own Blood
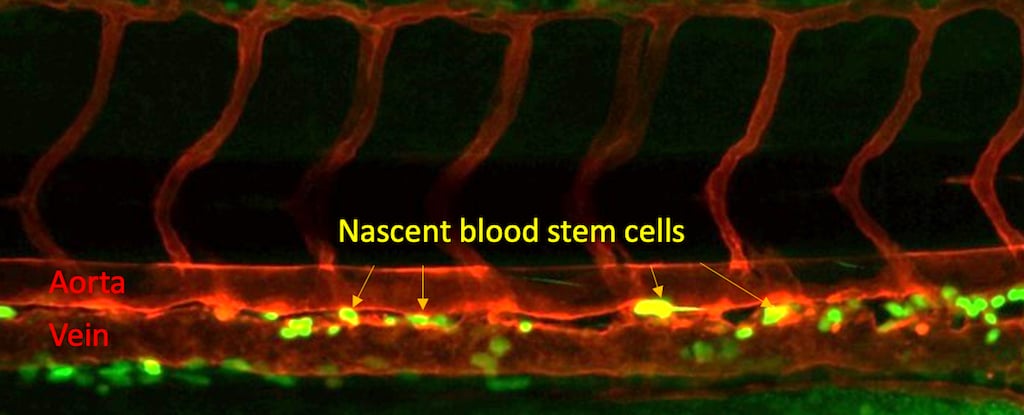
A new study has found that a protein receptor called Nod1, known for its role in recognizing bacterial infections, also plays a crucial role in the development of blood stem cells in embryos. This discovery could lead to the ability to produce blood stem cells from a person's own blood, potentially eliminating the need for bone marrow transplants and improving treatment for leukemia, lymphoma, and anemia patients. The research offers hope for regenerative medicine and could pave the way for creating therapeutic-grade blood stem cells to cure blood disorders.
