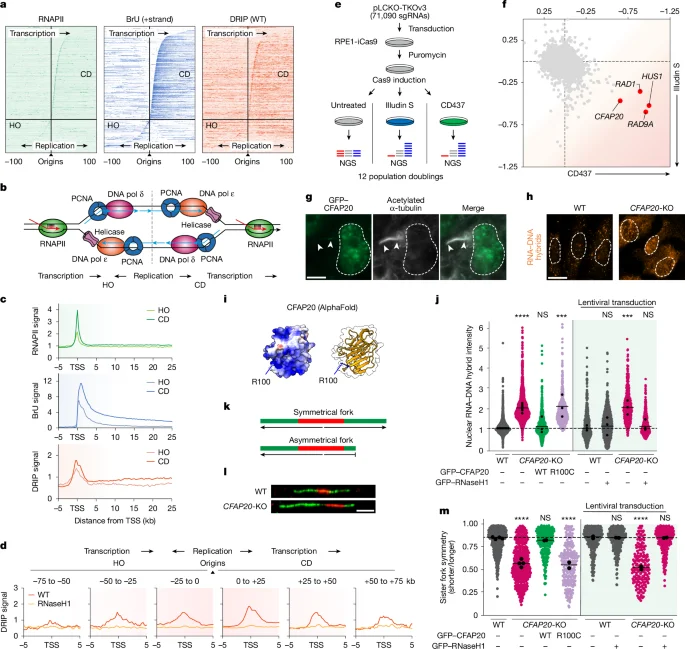
CFAP20 shields arrested RNAPII from replisome traffic at promoters
CFAP20 prevents promoter-proximal RNAPII arrest from causing clashes with co-directional replisomes, limiting R-loop buildup near replication origins and preserving replication timing. CFAP20 knockout raises promoter R-loops, speeds forks, and reduces origin firing—phenotypes that are rescued by restoring CFAP20 or by removing Mediator/CcNC activity. The protein appears to act in the nucleus to salvage arrested RNAPII, dampening Mediator-driven transcription stress to maintain genome stability.

