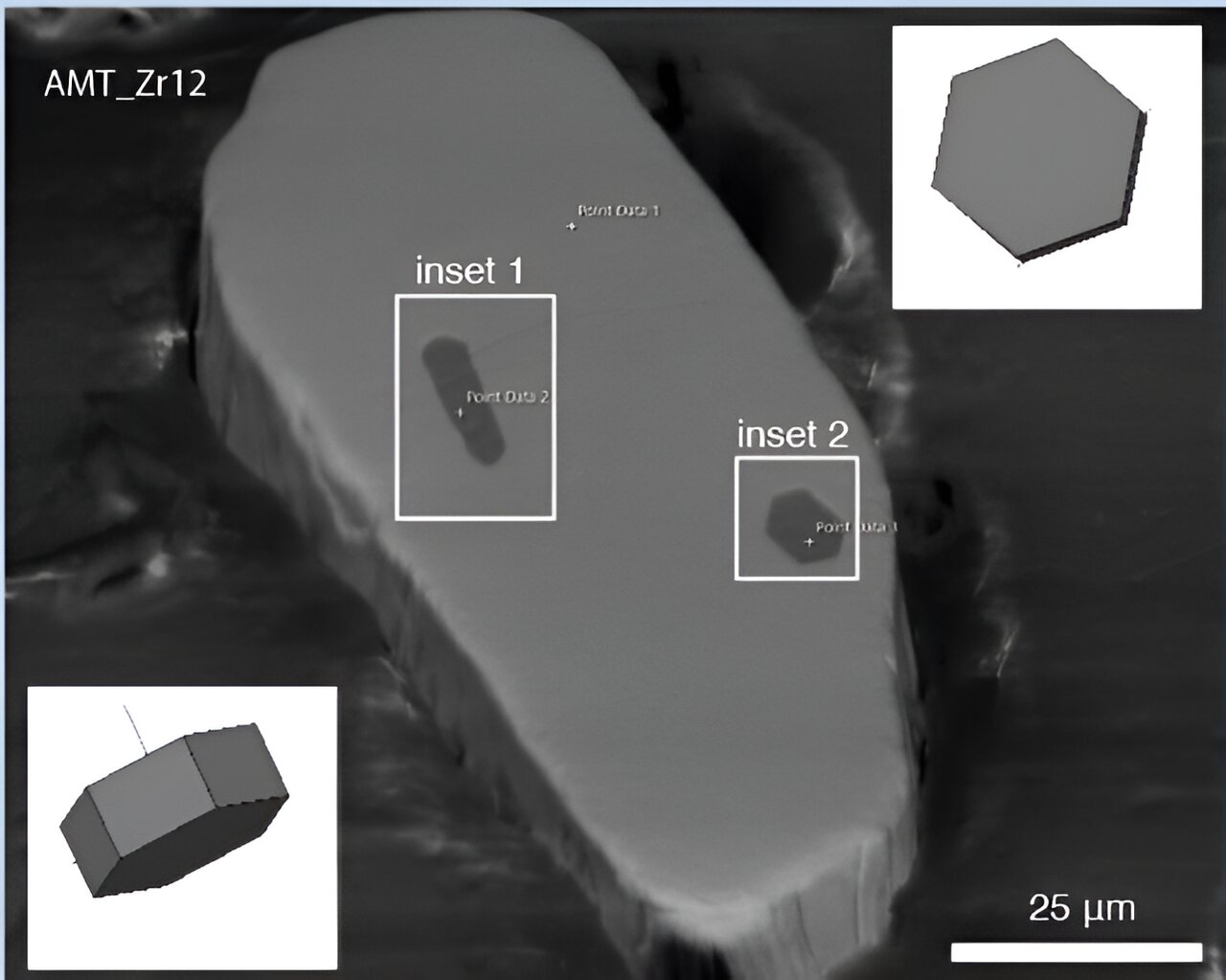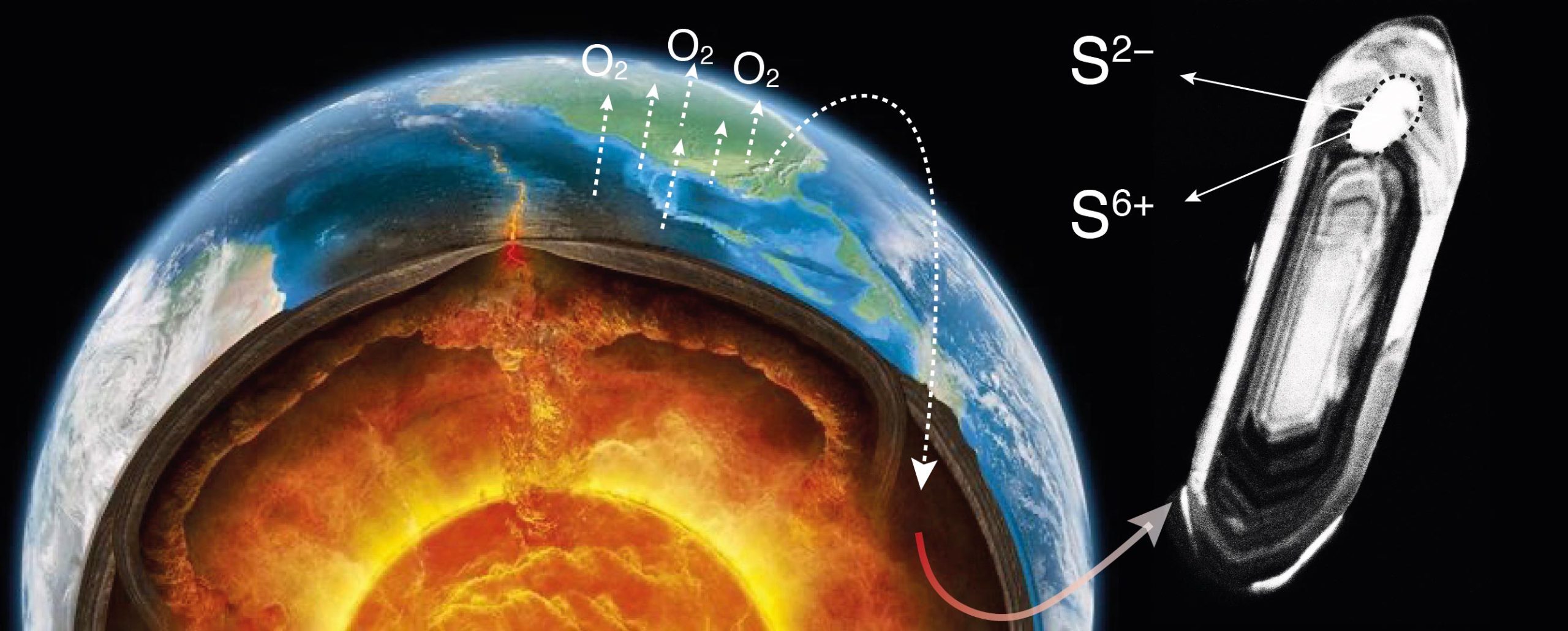
"Unveiling Earth's Ancient Breath: Startling Revelations from New Research"
New research has revealed a link between ancient atmospheric shifts and the chemistry of Earth's mantle, providing insights into the planet's evolution. The study focused on the Great Oxidation Event (GOE), a period when oxygen levels in Earth's atmosphere rapidly increased, and investigated magmas formed in ancient subduction zones. The findings suggest that sediment recycling played a crucial role in providing atmospheric access to the mantle, leading to increased oxidation of magma and altering the composition of the continental crust. This discovery sheds light on the relationship between Earth's external and internal reservoirs and raises questions about the role of oxygen in shaping the planet's history and the conditions for life.