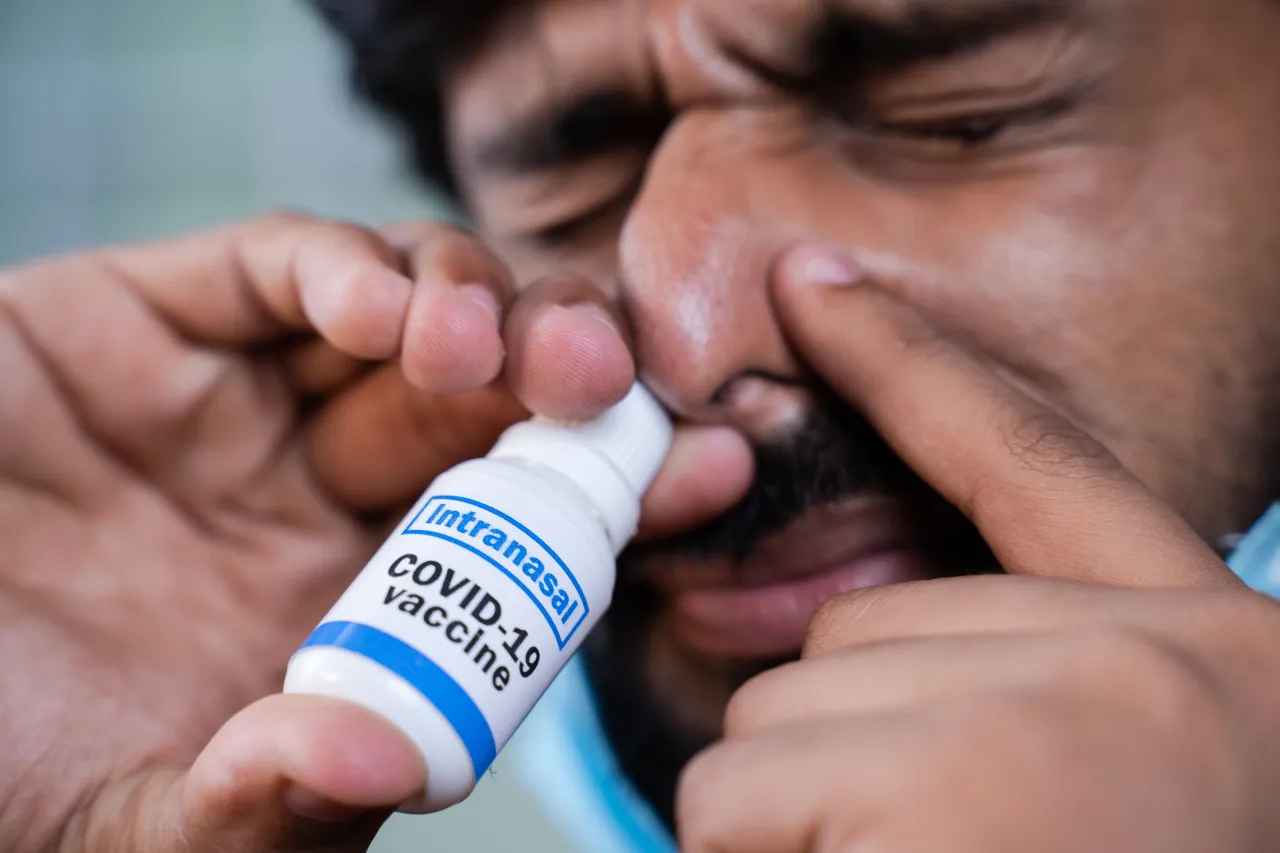
Promising Results for Intranasal COVID Vaccine in Early Trials
Codagenix has announced promising findings for its live-attenuated intranasal COVID vaccine candidate, CoviLiv, which prompted robust humoral and cellular immunity in adults during a phase 1 clinical trial. The vaccine, developed in collaboration with the Serum Institute of India, is currently undergoing a phase 3 efficacy trial as part of the WHO Solidarity vaccine trials. Intranasal vaccines are attractive for their needle-free formulation and potential to stimulate mucosal immunity. Codagenix's vaccine, which is easy to administer and doesn't require refrigeration, may be more appealing for use in low-resource settings. The vaccine mimics natural infection and induces a specific type of local immune response, potentially contributing to hybrid immunity.