"Discovery of HKDC1 Protein: A Potential Key to Halting Aging and Cellular Senescence"
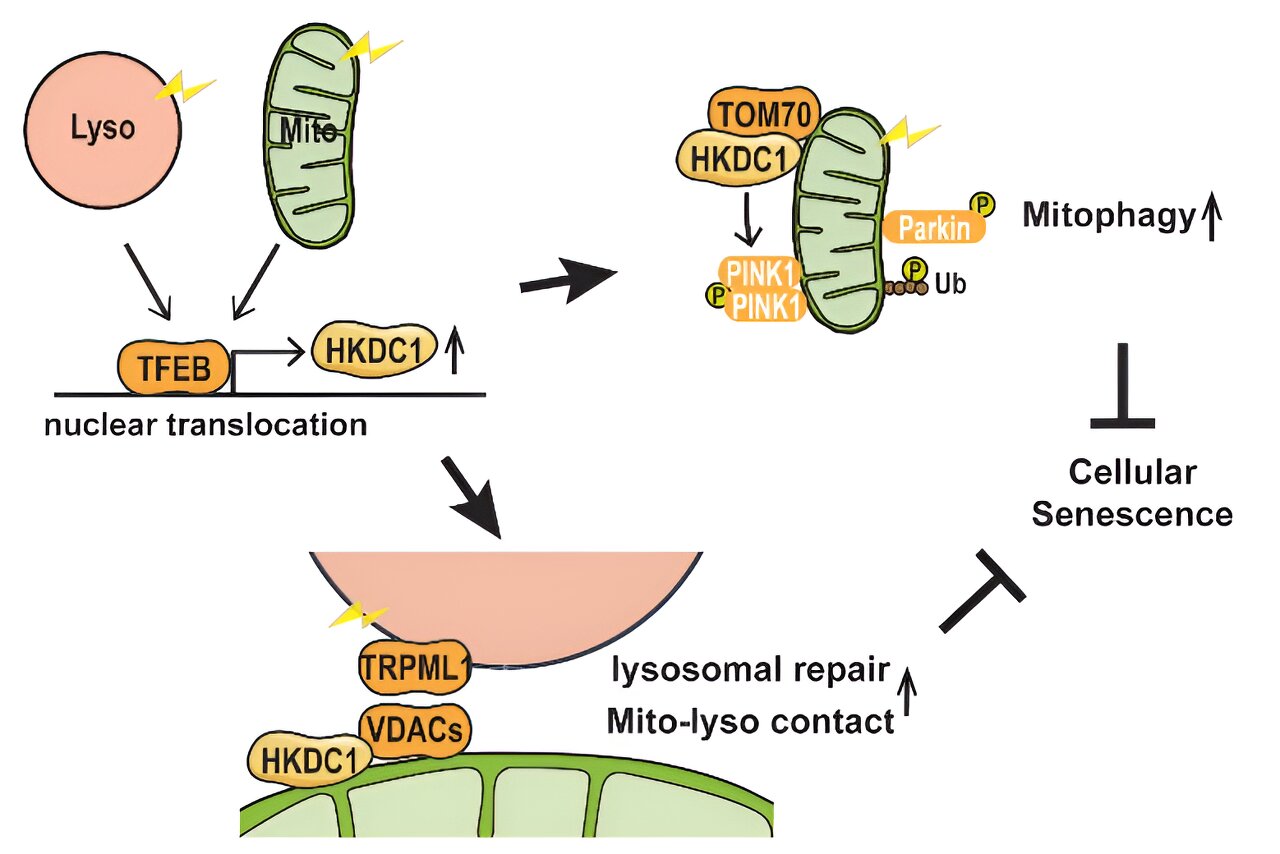
Japanese scientists have discovered a protein, hexokinase domain containing 1 (HKDC1), that helps maintain mitochondria and lysosomes, which are crucial for cell health and energy production. Damage to these organelles is associated with ageing and various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders. HKDC1's role in protecting these structures and preventing cellular senescence could lead to new treatments for age-related diseases and potentially impact lung and liver cancers. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, highlights HKDC1 as a potential target for developing senolytic drugs that combat cellular ageing.