Global Study Reveals Alarming Decline in Antibiotic Efficacy for Childhood Infections
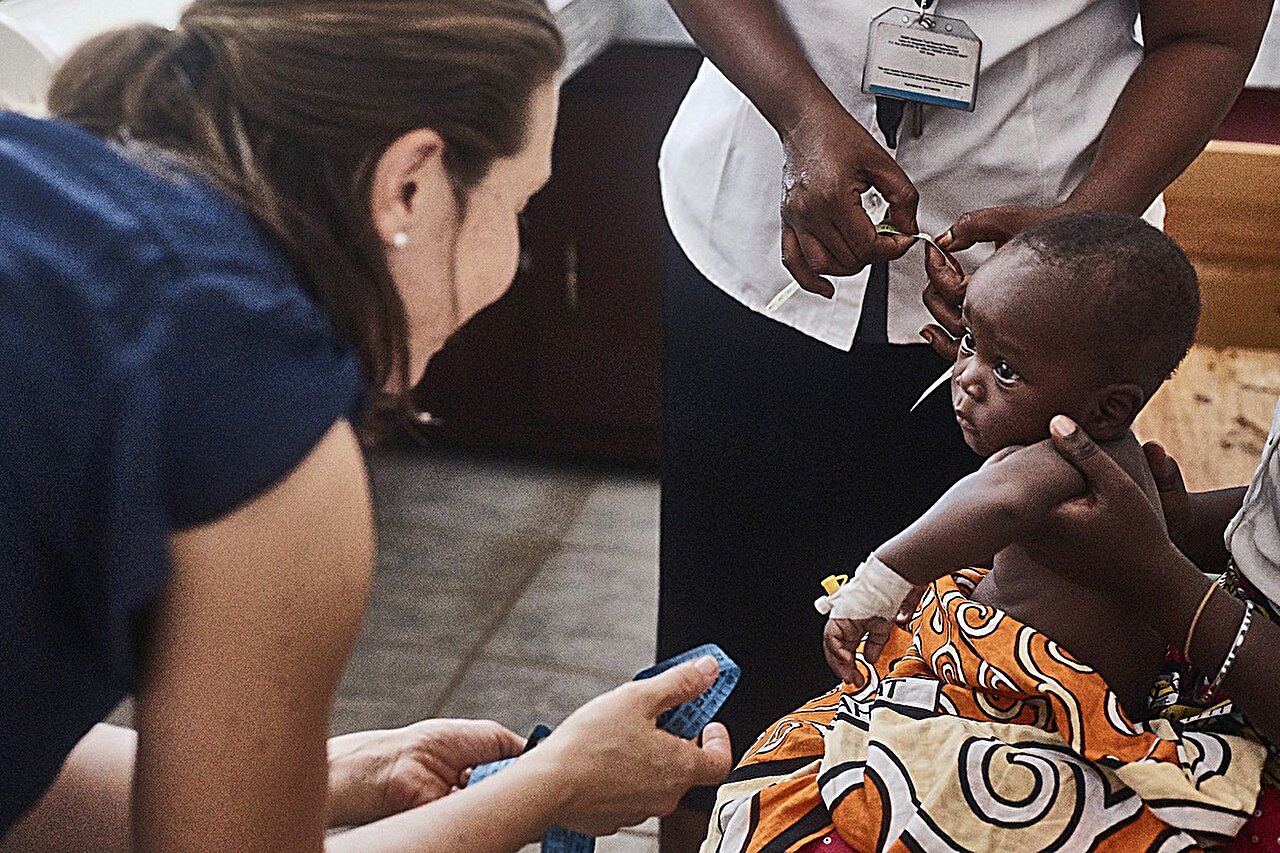
Antibiotics recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for treating common childhood infections such as pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis are no longer effective in many parts of the world due to high rates of antibiotic resistance. A study led by the University of Sydney found that these antibiotics had less than 50 percent effectiveness in treating these infections. The most affected regions are in South-East Asia and the Pacific, where thousands of unnecessary deaths in children occur each year. The study highlights the urgent need for updated global antibiotic guidelines to address the rapidly evolving rates of antimicrobial resistance.