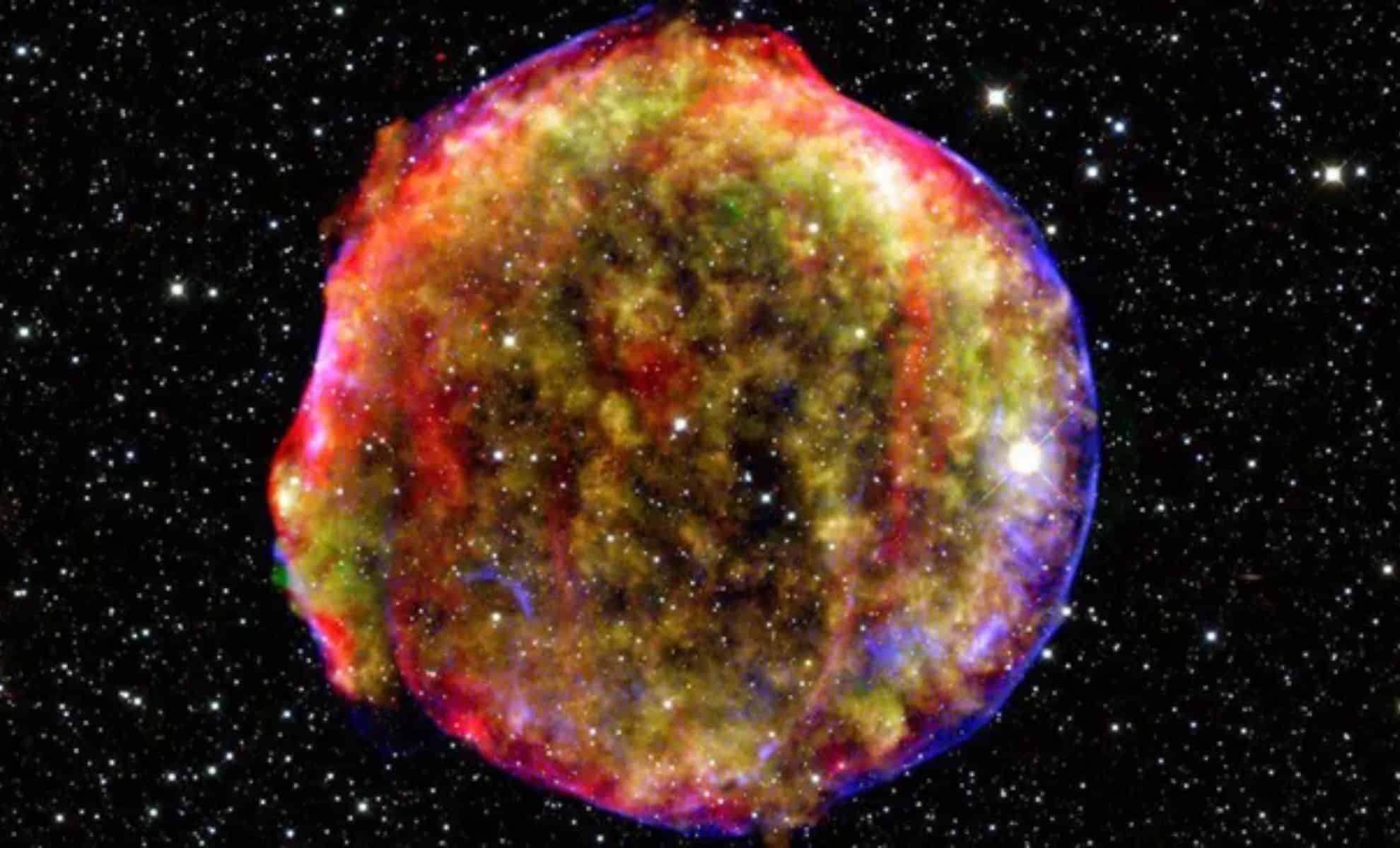
Exploding Star Behind Earth's Most Dangerous Radiation Source
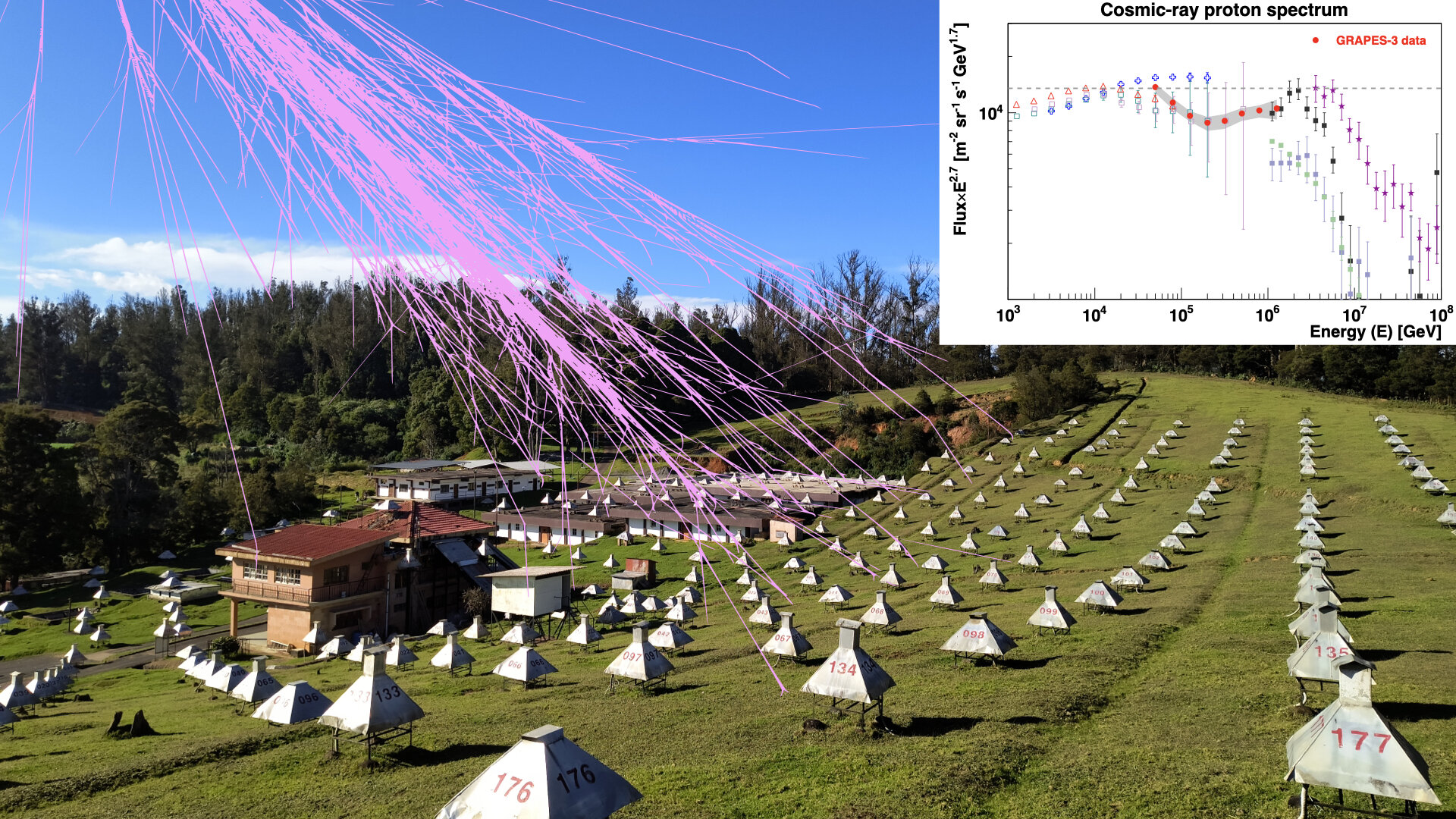
A new study suggests that supernova remnants can temporarily become the universe's most powerful particle accelerators, called PeVatrons, capable of producing ultra-energetic cosmic rays. This phase is brief, lasting only a few months, which explains why direct detections are rare despite frequent supernovae in the Milky Way. The key factor is the dense gas shell around the star, which, when hit by the explosion, creates intense magnetic fields that accelerate particles to PeV energies.