"Uncovering the Connection: Cold Snaps and Pandemics in the Roman Empire"
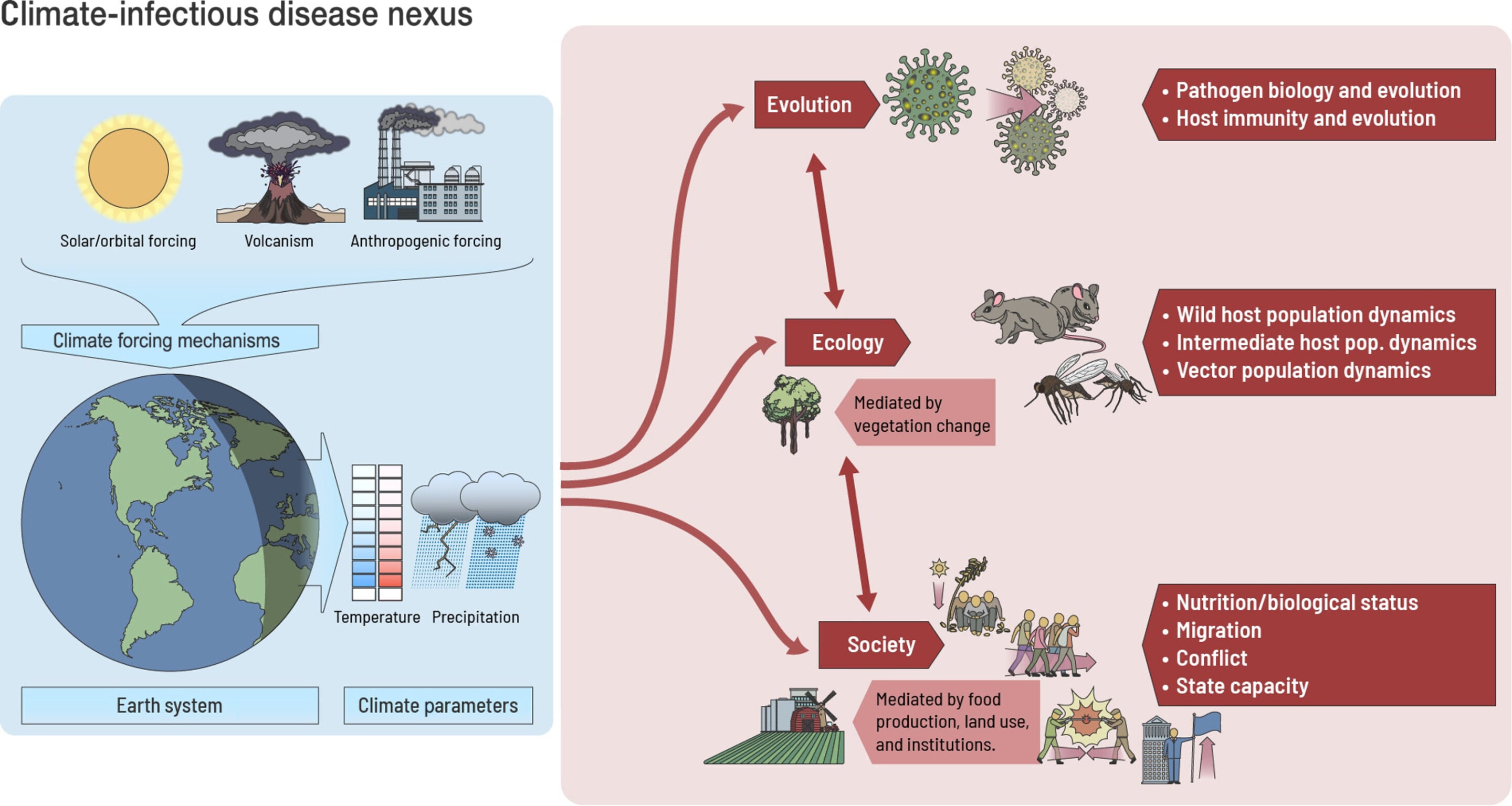
A team of geoscientists has discovered a link between cold snaps and pandemics during the Roman Empire by studying core samples from the seabed in the Gulf of Taranto. The researchers found that cold snaps, which occurred during the period 200 B.C. to 600 A.D., coincided with pandemics, suggesting that weakened immune systems due to the cold and food scarcity may have contributed to the spread of diseases. This study sheds light on the potential impact of climate change on societal health during ancient times.

