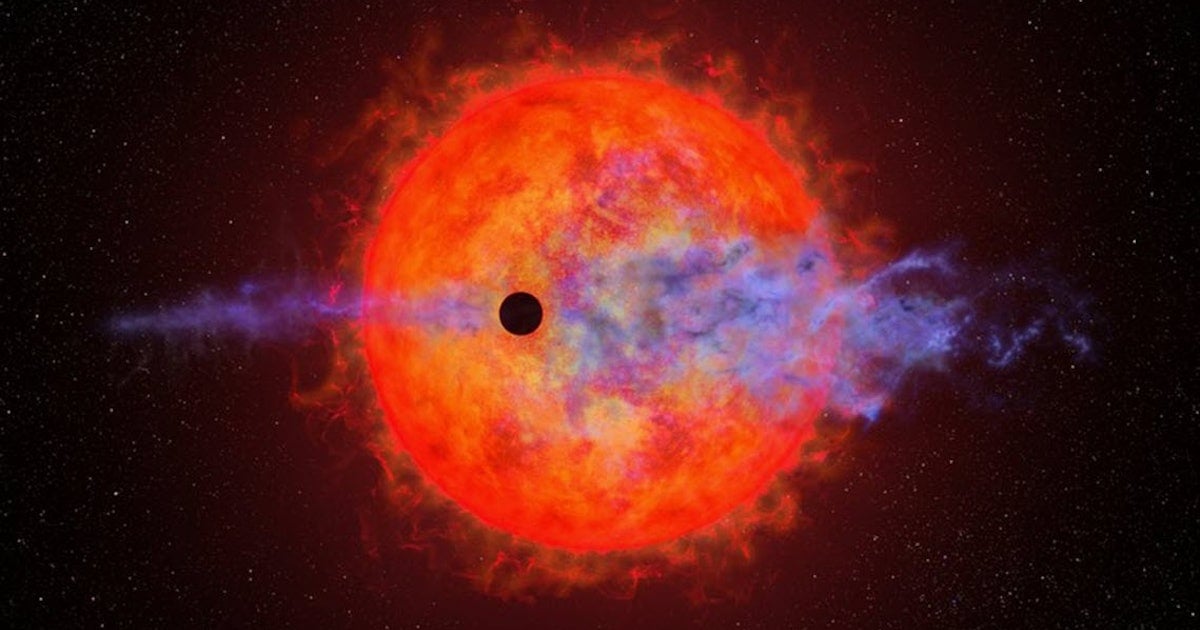
"Unveiling the Violent Birth of a Planet: Astronomers Witness Atmosphere Being Stripped Away"
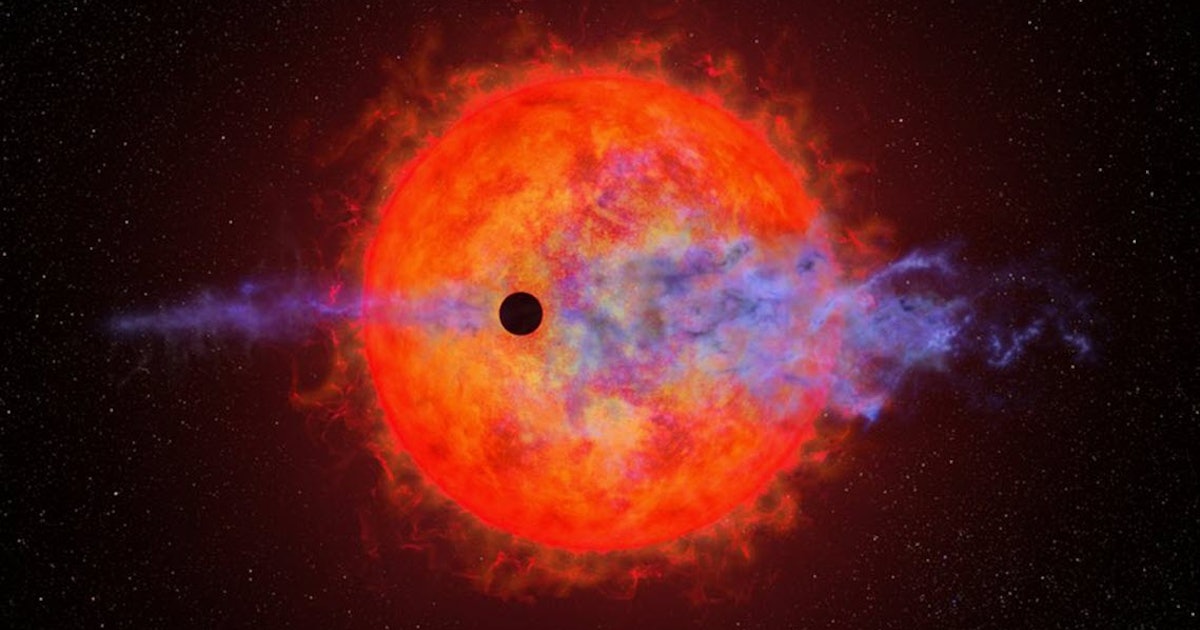
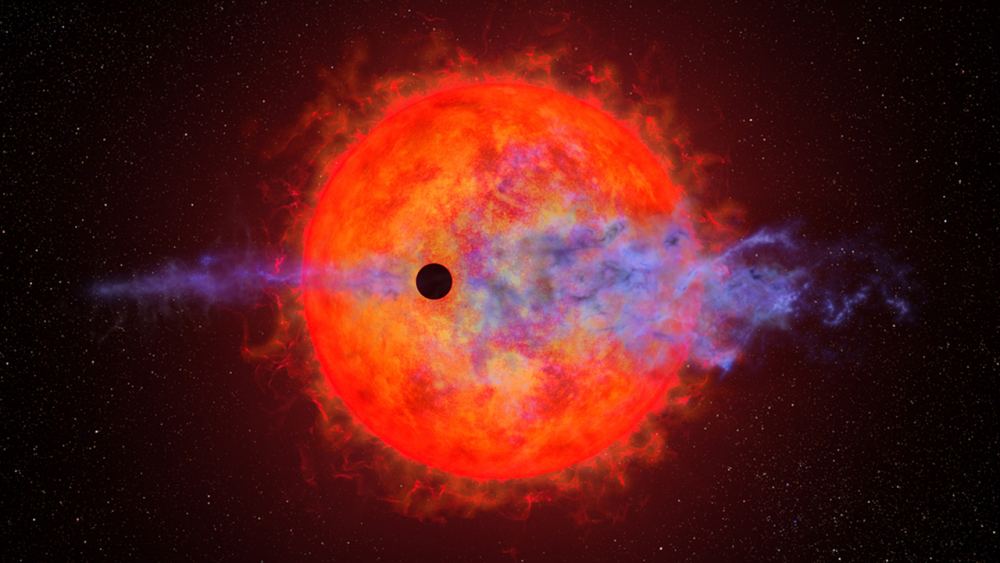
Astronomers have observed the Neptune-sized planet AU Microscopii b losing its atmosphere in a highly variable and unpredictable manner due to the intense flaring activity of its young red dwarf star. The planet's hydrogen atmosphere is being torn away in fits and starts, with periods of significant loss followed by minimal loss. This unusual behavior raises questions about the survivability and habitability of planets close to red dwarfs. Further observations are needed to understand the mechanisms behind this atmospheric loss and its implications for exoplanet compositions and potential habitability.


