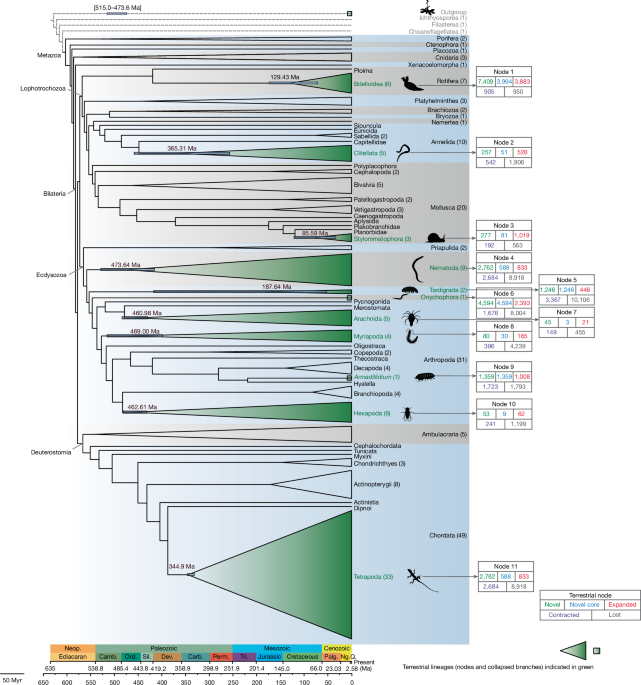
Genomic convergence drove the rise of land animals
The study reveals that independent terrestrialization events in animals involved convergent genomic adaptations, including gene gains and losses related to osmoregulation, stress response, immunity, and sensory functions, with three major temporal windows identified during Earth's history, highlighting both predictable and lineage-specific evolutionary responses to land colonization.
