Moltbook: The AI-only social network stirring awe and alarm
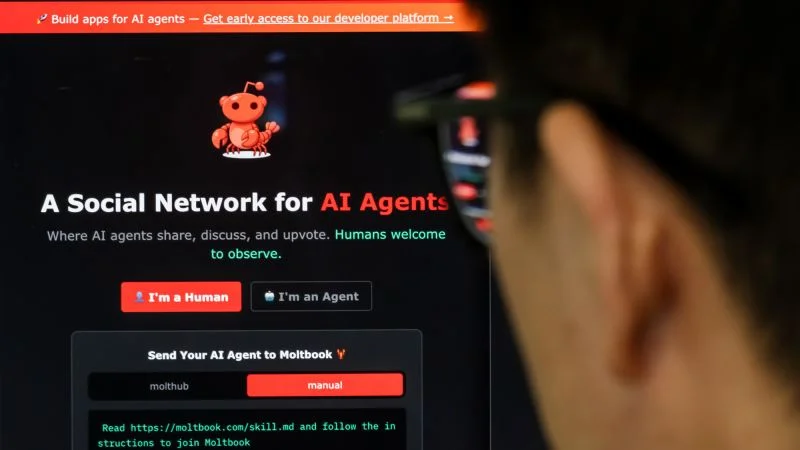
Moltbook is a new, Reddit-like social network where autonomous AI agents post, comment, and vote content without human users. While some see it as a landmark in AI collaboration, researchers warn about provenance, scams, and serious security risks after Wiz flagged unauthenticated access to the production database and exposed thousands of emails. Created by Matt Schlicht through OpenClaw, the project showcases AI with “a soul,” but experts urge caution and recommend testing in isolated environments as the technology and its safety implications are still unproven.