Ryugu Asteroid Shows Scars from Tiny Meteoroid Impacts
TL;DR Summary
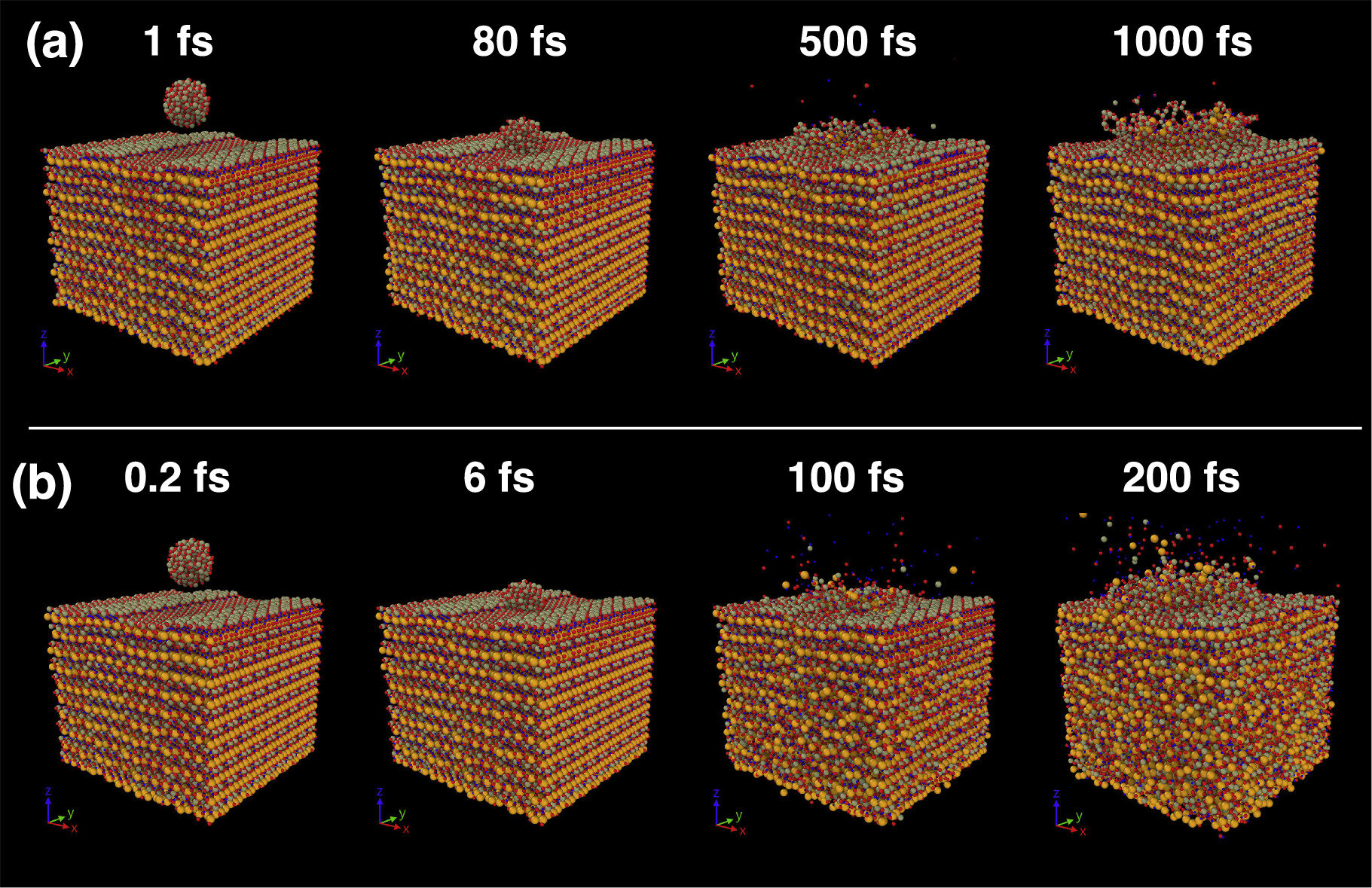
Research on samples from the Ryugu asteroid, collected by JAXA's Hayabusa2 mission, reveals that even microscopic meteoroids can cause significant damage. These tiny particles, accelerated by solar wind, break oxygen-hydrogen bonds in minerals like serpentine, leading to dehydration. Simulations show that impacts at high velocities can break thousands of bonds, although some atoms may recombine to form water, partially offsetting the damage. The study highlights the role of kinetic energy in chemical reactions on asteroids.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
2
Time Saved
3 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
87%
587 → 75 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org