The Role of Extrachromosomal DNA in Early Cancer Formation.
TL;DR Summary
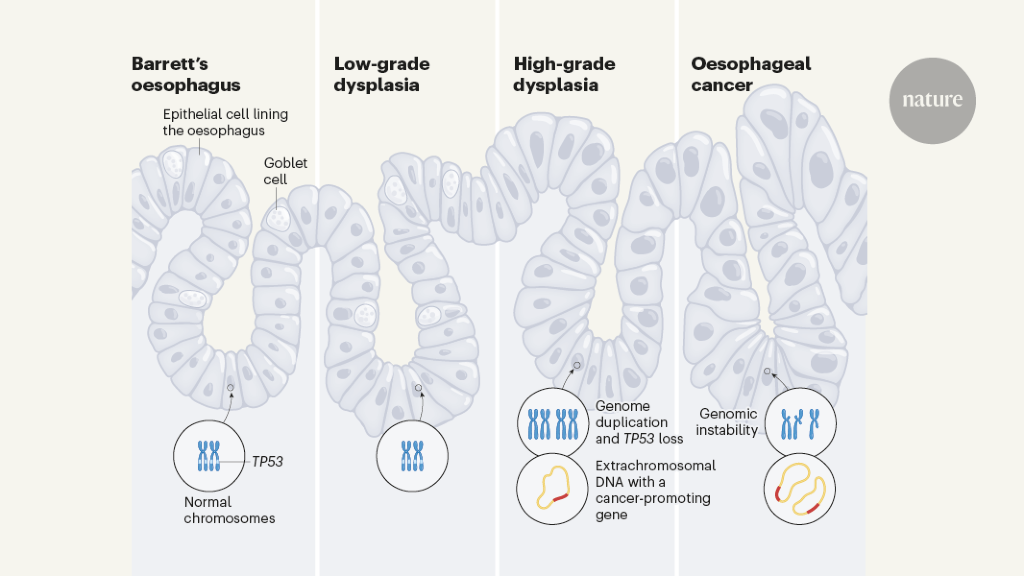
Extrachromosomal DNA, a circular DNA not found on chromosomes, was previously thought to be exclusive to cancer. However, a recent study found extrachromosomal DNA in non-cancerous oesophageal tissue that is predisposed to cancer development, suggesting it may have an early active role in malignant transformation. This type of DNA can aid cancer growth by harbouring cancer-promoting genes and boosting the efficiency of its transcription, leading to rapid amplification of oncogene content and tumour evolution.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
7
Time Saved
2 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
83%
438 → 74 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com