Understanding Tissue-Resident Macrophages and Their Role in Disease.
TL;DR Summary
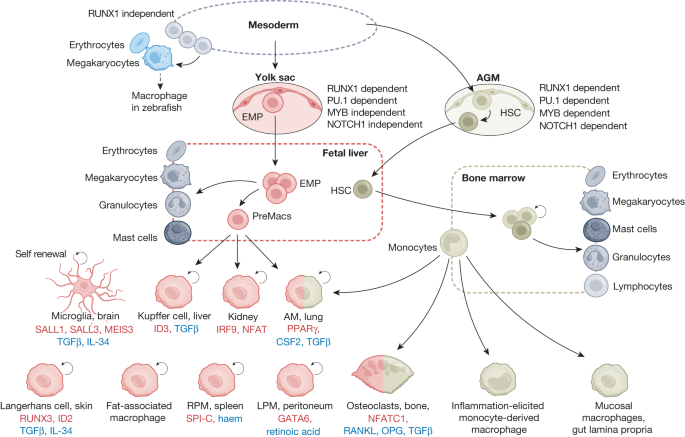
Macrophages are a diverse group of immune cells that play crucial roles in tissue homeostasis, development, and immunity. Recent studies have shown that tissue-resident macrophages originate from embryonic precursors and self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Macrophages also have important functions in tissue growth and repair, as well as in regulating salt-dependent volume and blood pressure. They sense their environment through various receptors and respond to stimuli such as hypoxia and mechanical force.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
6
Time Saved
26 min
vs 27 min read
Condensed
99%
5,264 → 78 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com