New Gut 'Sense' Links Microbes to Hunger, Brain, and Weight Loss
TL;DR Summary
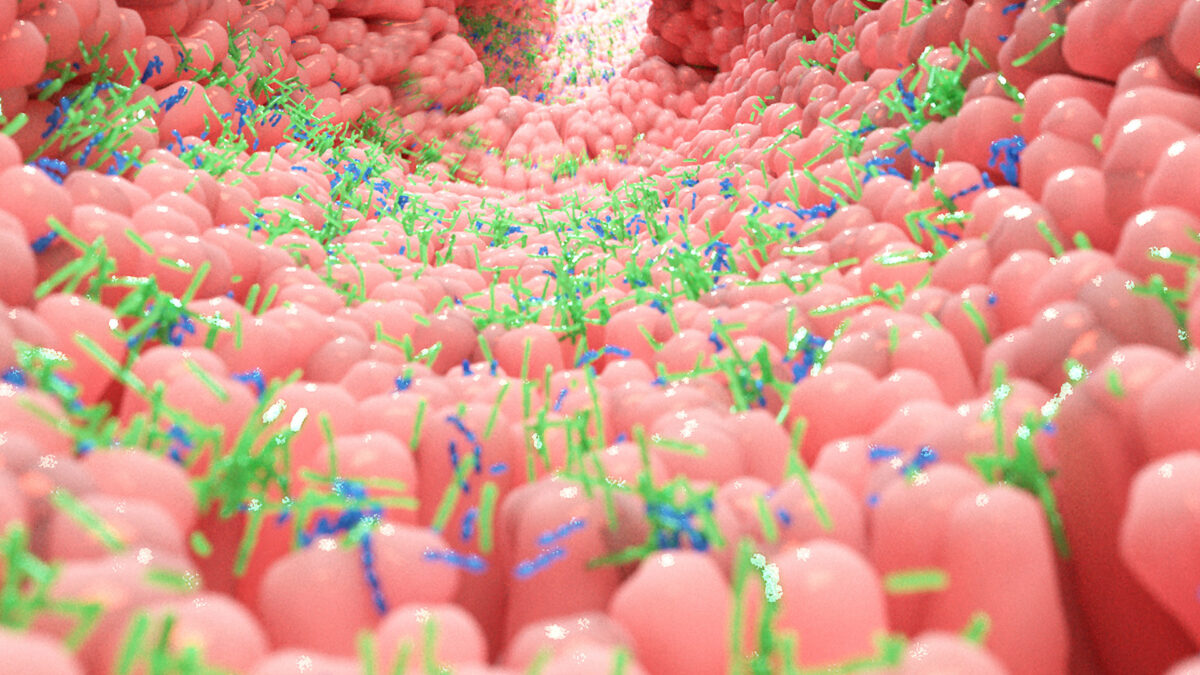
Researchers at Duke University have discovered a potential new 'sense' in the gut involving nerve cells called neuropods that detect bacterial signals, specifically flagellin, and communicate with the brain via the vagus nerve to regulate hunger, suggesting a complex gut-brain-microbiome connection that could have significant health implications.
- Newly Discovered Gut ‘Sense’ Could Change How We Think About Hunger and Health Gizmodo
- A gut sense for a microbial pattern regulates feeding Nature
- Your colon’s got a ‘sixth sense’ — here’s how it can lead to weight loss New York Post
- An Extra Sense May Connect Gut Bacteria With Our Brain ScienceAlert
- Probiotic bacteria found to reshape cell behavior in vitro News-Medical
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
3 min
vs 4 min read
Condensed
92%
612 → 47 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Gizmodo