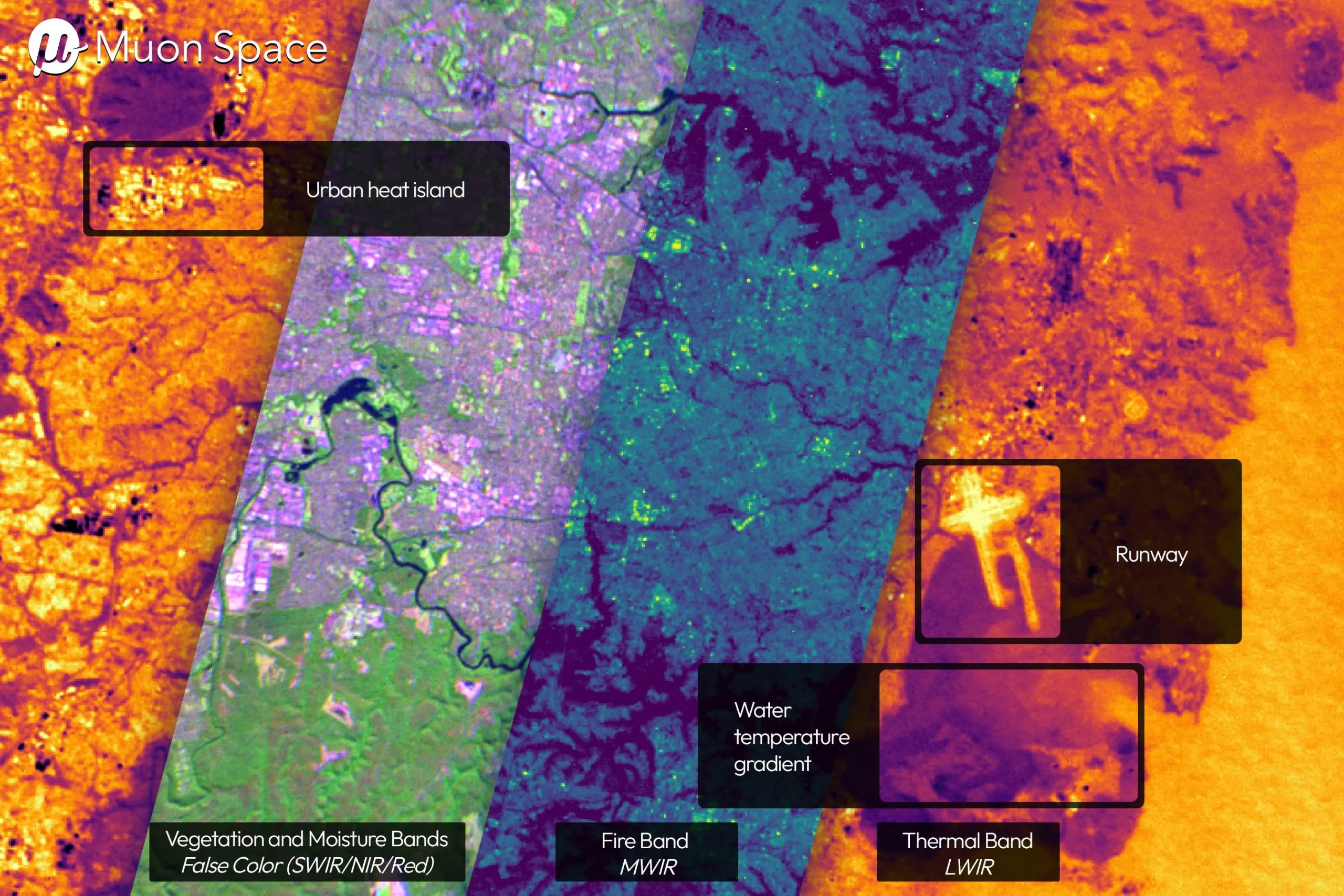
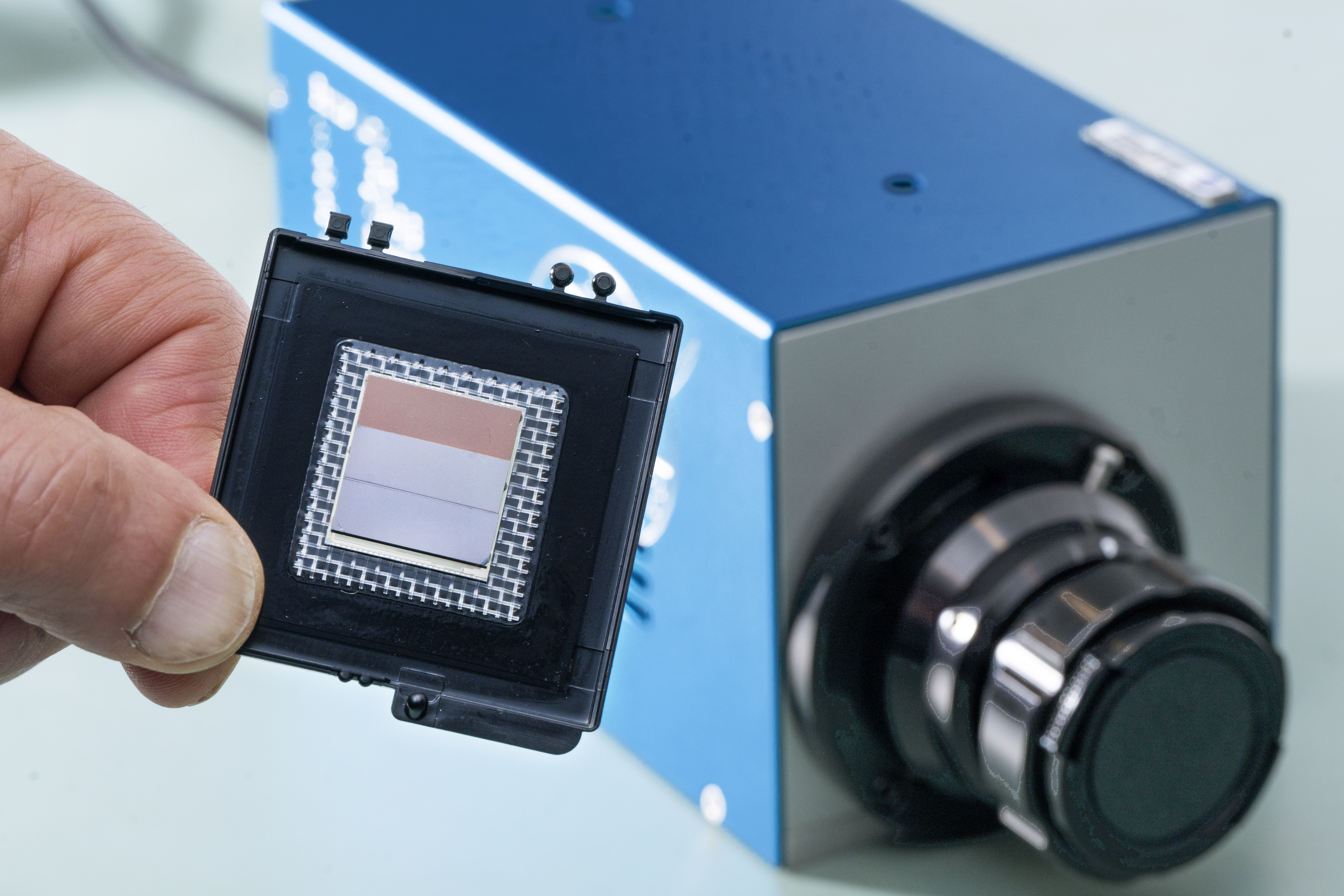
New Satellite Network to Detect Wildfires Every 20 Minutes
Muon Space has launched its FireSat satellite, the first in a planned constellation of over 50 satellites designed to scan the entire Earth every 20 minutes to detect wildfires using multi-band infrared sensors, aiming to improve wildfire response and mitigation.