"Breakthrough in Pressure Measurement: Introducing the Ultimate 'Primary Standard' for Ultralow Pressures"
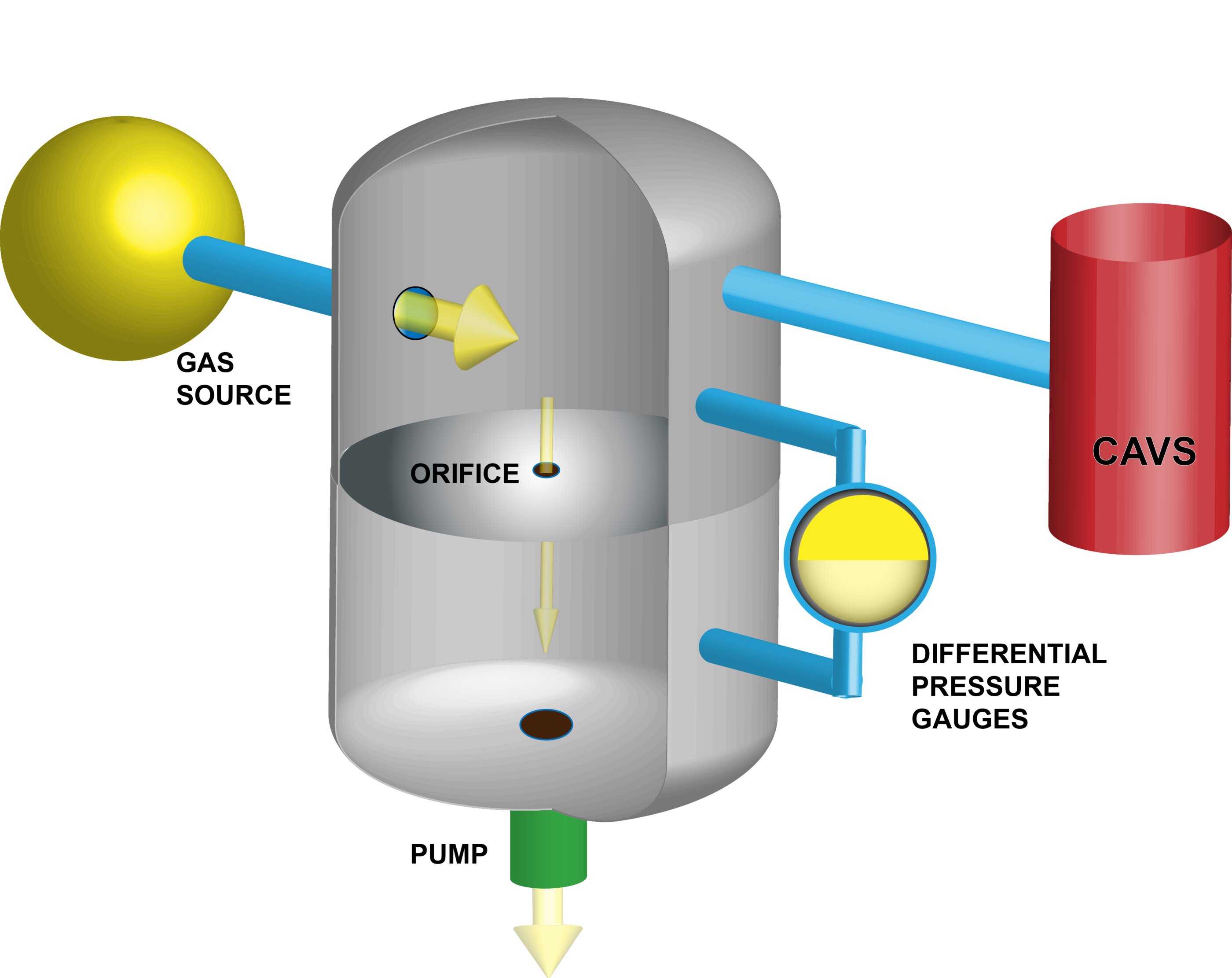
Scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a new technique called CAVS (cold atom vacuum standard) for measuring extremely low gas pressures. The CAVS method has been validated as a "primary standard," meaning it can make accurate measurements without needing to be calibrated to reference pressure readings. The technique uses a cold gas of lithium or rubidium atoms trapped in a magnetic field, and the intensity of light emitted by the atoms serves as a measure of pressure. CAVS can measure vacuum pressures as low as a trillionth of the Earth's atmospheric pressure and has applications in semiconductor manufacturing, quantum computers, gravitational wave detectors, and particle accelerators.

