Anthropic rolls out AI-assisted code security with human-in-the-loop patches
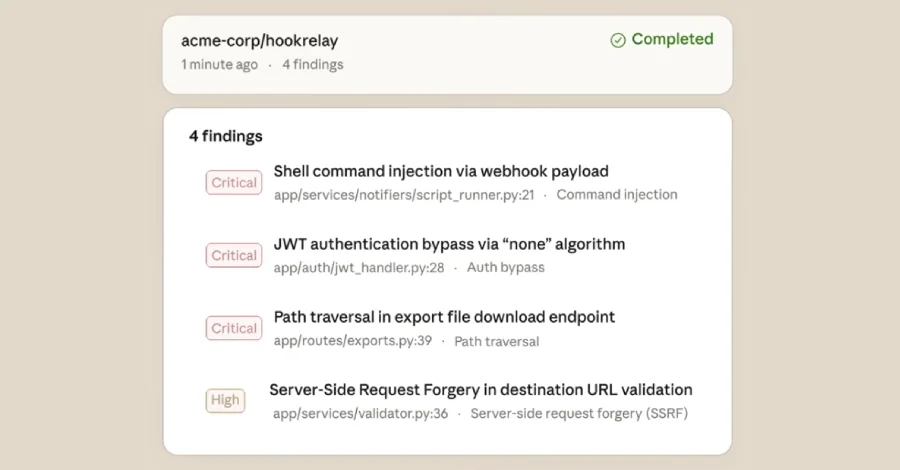
Anthropic is rolling out Claude Code Security in a limited research preview for Enterprise and Team customers, offering AI-driven scanning of codebases to find vulnerabilities and propose patches for human review. The tool reasons about code interactions and data flows beyond static checks, uses a multi-stage verification to reduce false positives, and assigns severities; results appear in a dashboard and require human approval before changes are applied, aiming to help defenders counter AI-enabled attacks.