"Unleashing the Power of Graphene: A Game-Changer for Renewable Energy"
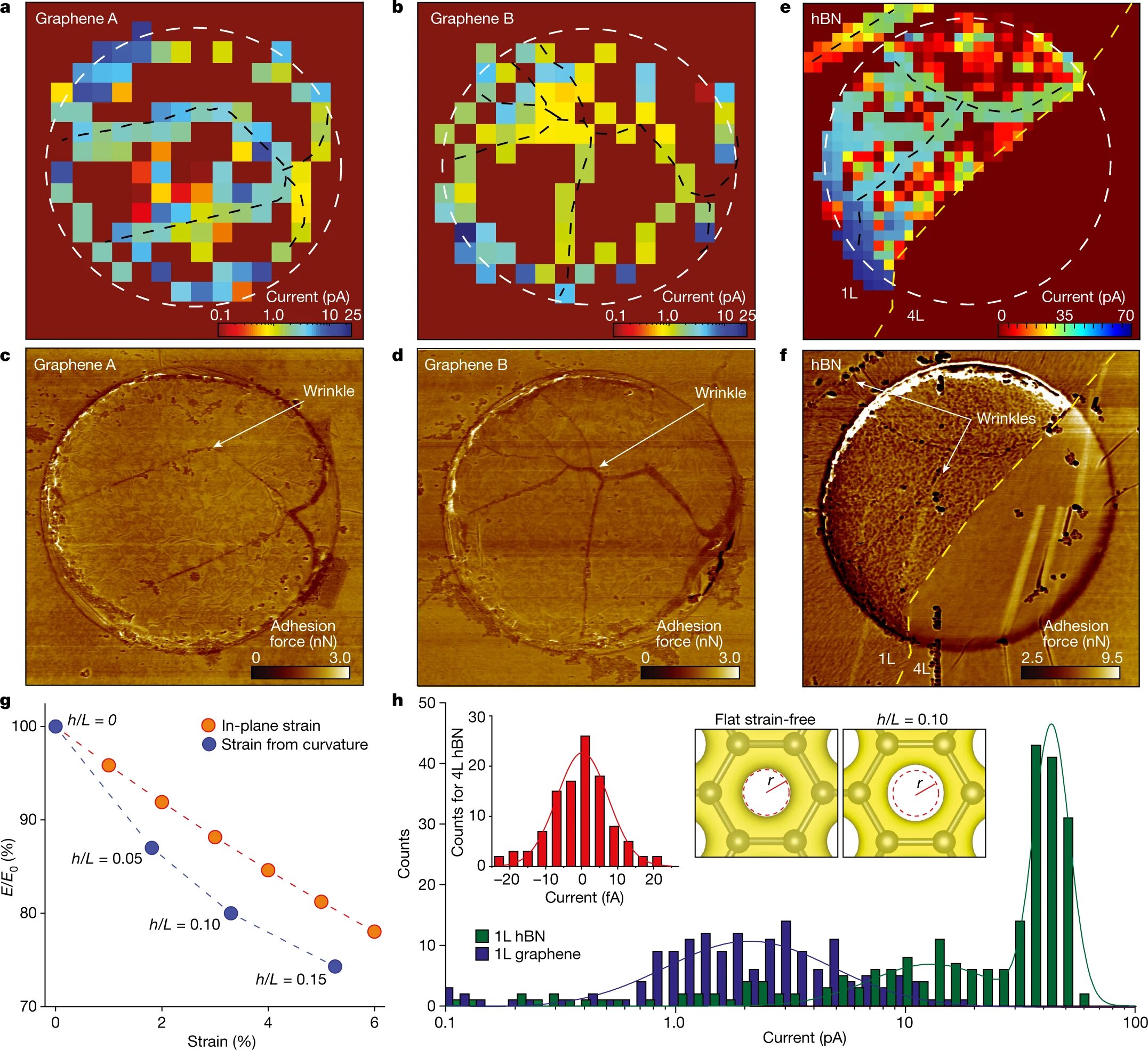
Researchers at the University of Manchester's National Graphene Institute have discovered a method to accelerate proton transport through graphene using light. This breakthrough could have significant implications for the development of renewable energy, particularly in the production of green hydrogen. Graphene's unique structure allows for the diffusion of protons through its edges, flaws, and functionalization, and the use of light can enhance this process, opening up new possibilities for clean energy technologies.