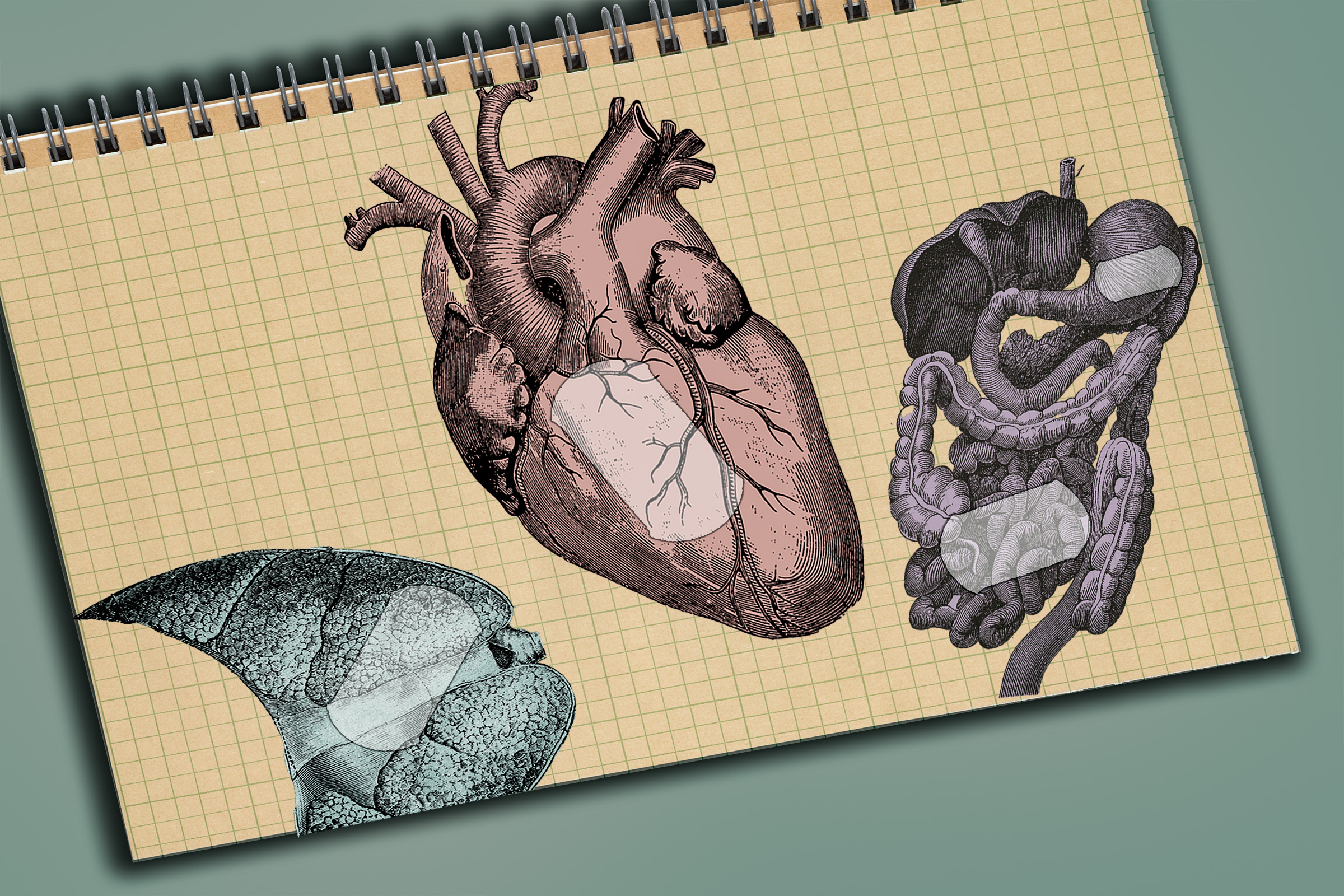
MIT's Hydrogel 'Invisibility Cloak' Prevents Implant Scarring
MIT engineers have developed a hydrogel adhesive coating for medical implants that prevents fibrosis, or scar tissue formation, which can interfere with device function. This adhesive binds the devices to tissue, preventing the immune system from attacking them. The approach has shown success in animal models and could be used for various implants, including pacemakers and drug delivery devices. The research, published in Nature, was funded by the NIH and NSF.
