Unveiling the Neural Mechanisms of Survival during Fasting
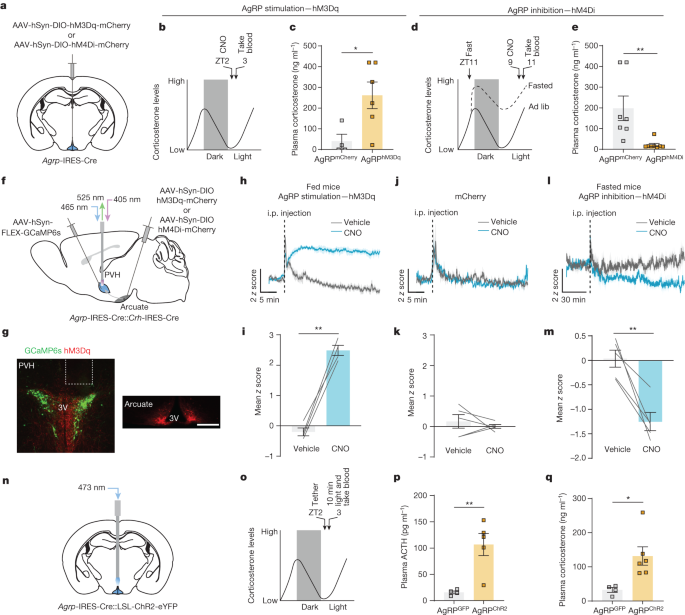
Researchers have identified the neural basis for the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during fasting. Using fibre photometry, they observed increased activity in AgRP neurons in the hypothalamus, which led to the release of neuropeptide Y (NPY) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This activation of AgRP neurons was found to be independent of feeding behavior and was mediated by the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R). The study provides insights into the neuroendocrine response to fasting and sheds light on the regulation of the HPA axis. Data and code availability are provided for further research.
