"Unveiling the Enormous Size of the Universe's Largest Star"
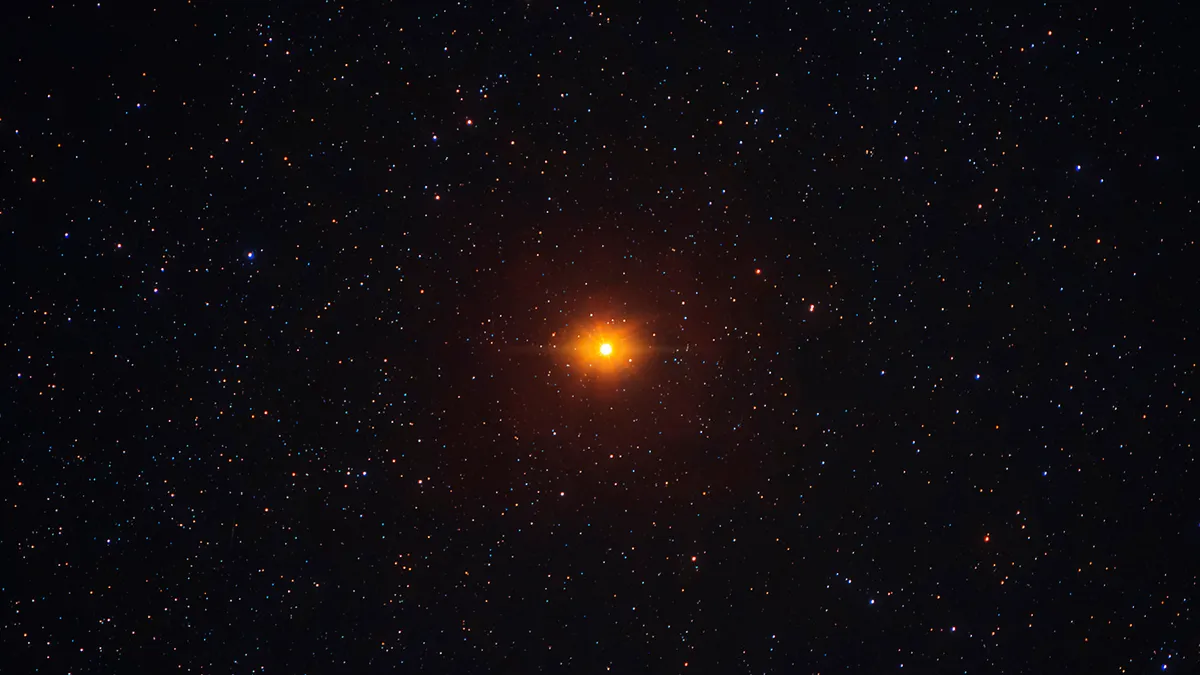
UY Scuti, a red supergiant star, holds the title of the largest known star in the universe, with a radius about 1,700 times larger than that of our Sun. Its immense size challenges our understanding of stellar physics, and if placed at the center of our solar system, it would engulf the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and potentially even Jupiter. Eta Carinae, a luminous blue variable star, is the brightest star in the universe in terms of intrinsic luminosity, while R136a1, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, is currently the heaviest star, challenging previous theories on stellar mass limits.