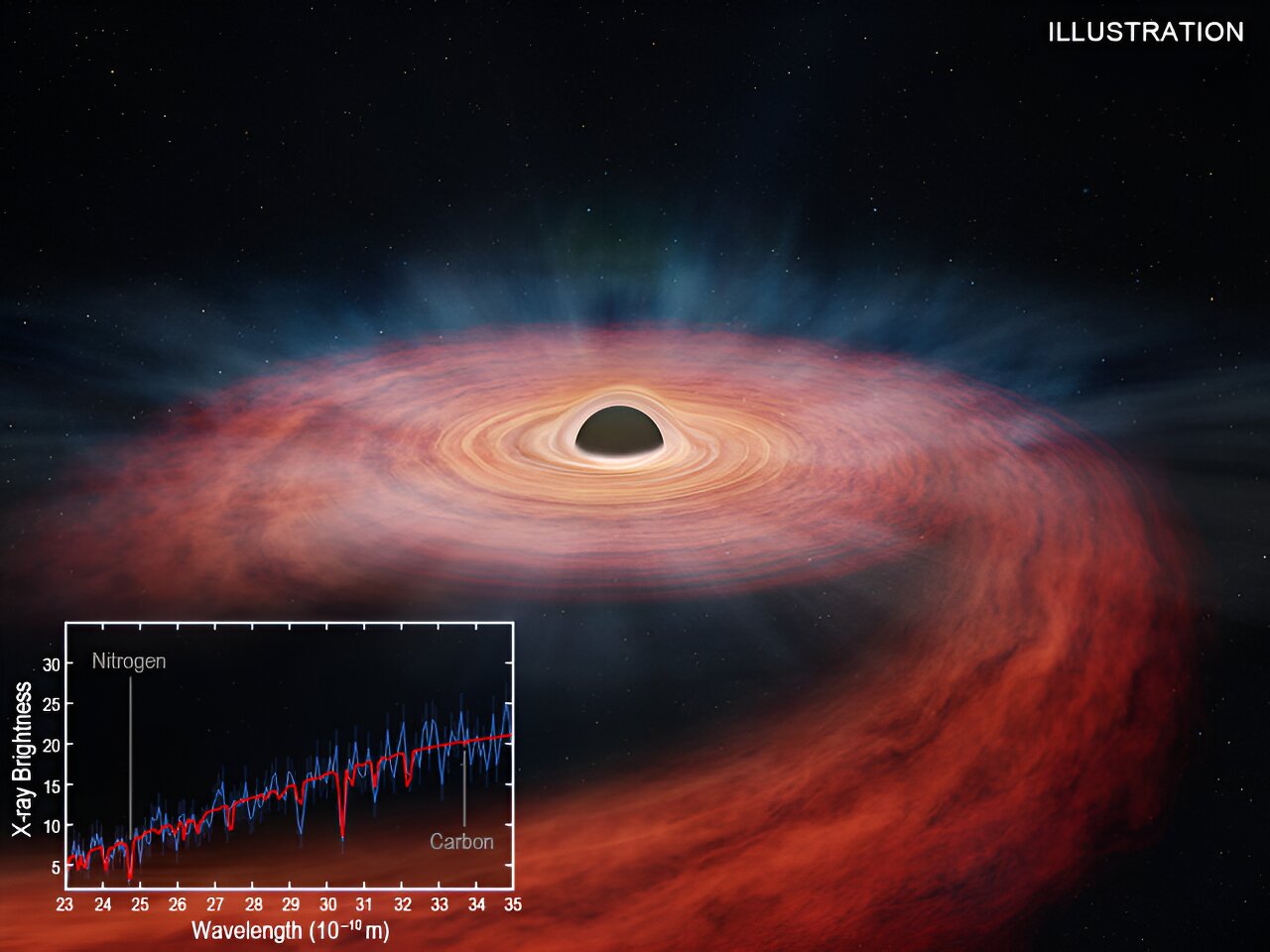
Black Hole Devours Massive Star, Ejects Stellar Debris
Astronomers have studied the aftermath of a tidal disruption event known as ASASSN-14li, where a massive star was torn apart by a giant black hole. NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and ESA's XMM-Newton analyzed the nitrogen and carbon near the black hole, providing clues about the star's composition. The star in ASASSN-14li was estimated to have three times the mass of the Sun, making it one of the most massive stars observed to be destroyed by a black hole. This study enhances our understanding of tidal disruptions and offers insights into the presence of star clusters around supermassive black holes in distant galaxies.
