Arctic Warming Sparks Sudden Ecosystem Change in North America's Deepest Lake
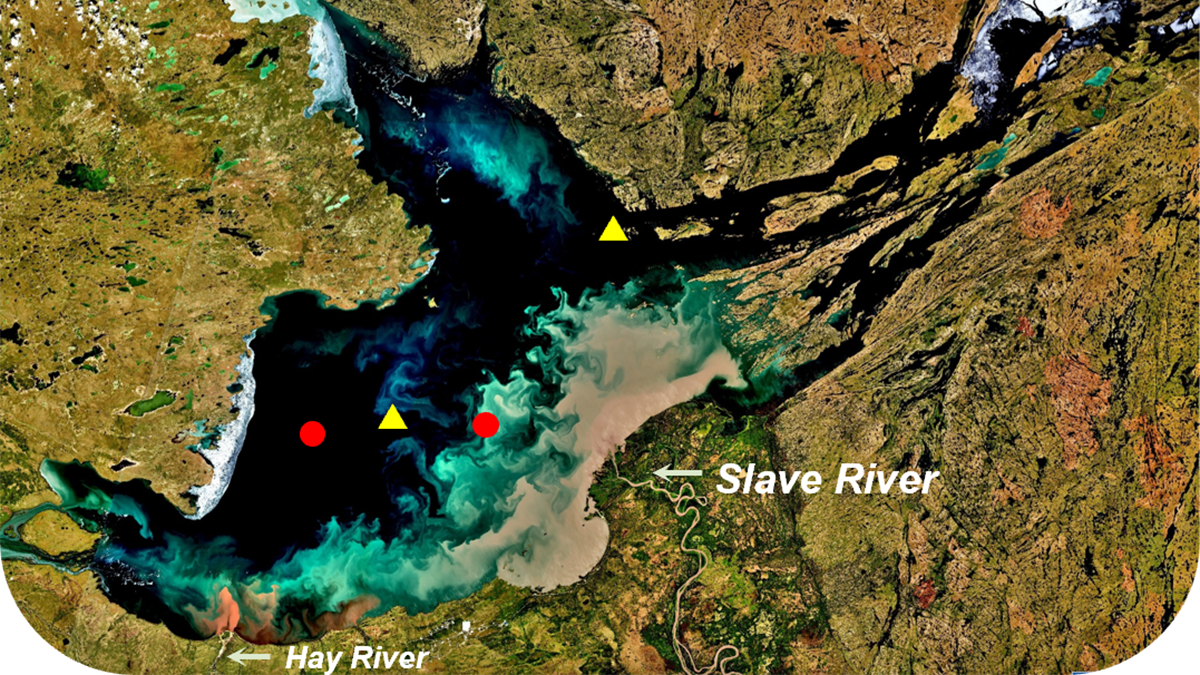
The warming Arctic climate has triggered a radical ecosystem shift in Great Slave Lake, North America's deepest lake. The microscopic algae, or phytoplankton, at the base of the lake's food web have undergone a regime change, with larger diatoms being replaced by smaller, pancake-shaped counterparts. This shift could impact the lake's productivity, carbon dynamics, and food web, affecting nearby communities that rely on the lake as a food and cultural resource. The transformation is attributed to rising temperatures, declining ice cover, and slowing winds in the region. Similar changes are also observed in Great Bear Lake.
