Unveiling the Universal Mechanisms of DNA and RNA Deformations
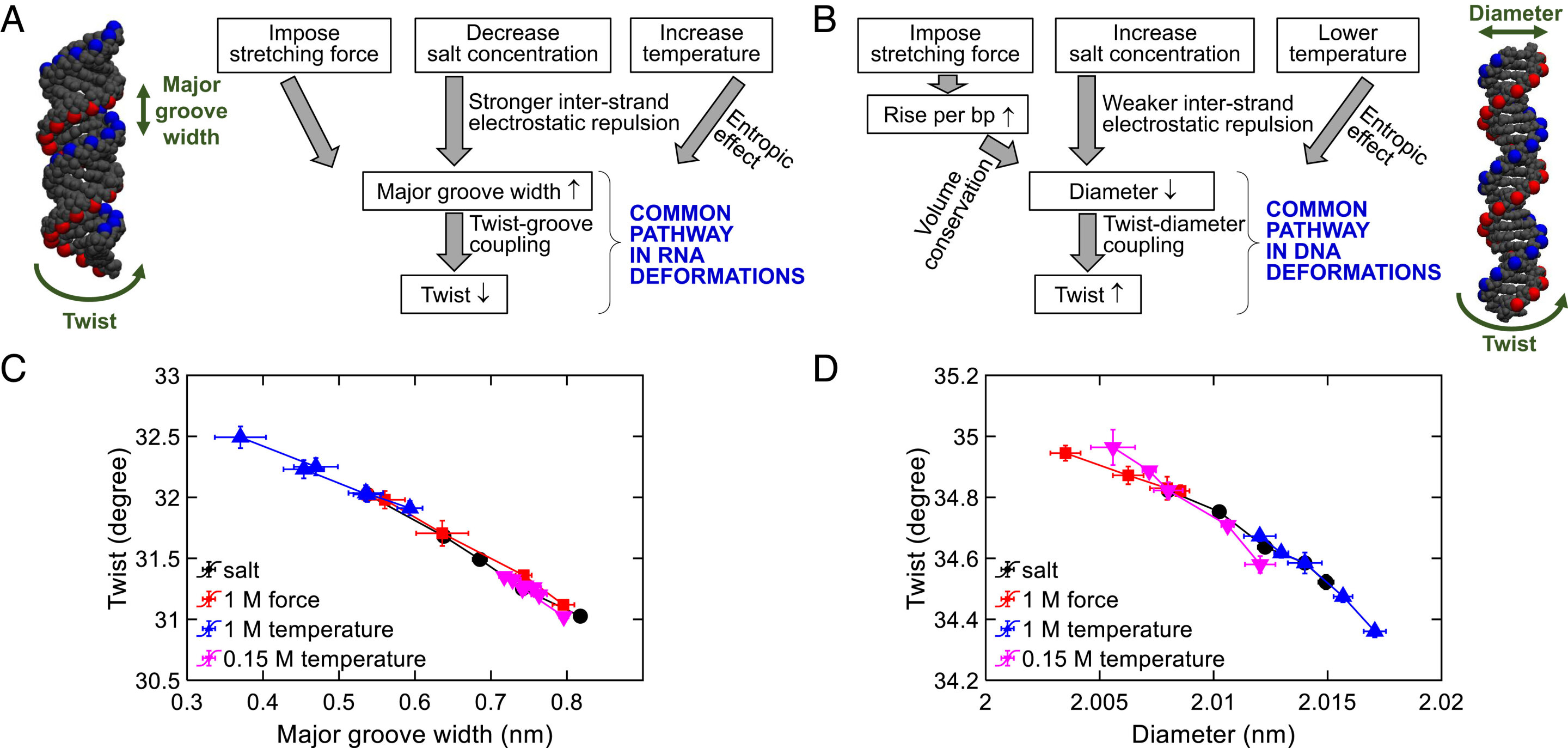
Researchers have identified common pathways of deformation in DNA and RNA, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms of these nucleic acids. Using magnetic tweezers, the team accurately measured the twist changes induced by salt, temperature change, and stretching force. They found that DNA deformations are driven by twist-diameter coupling, while RNA deformations are driven by twist-groove coupling. These universal deformation mechanisms can be applied to different types of nucleic acids and environmental stimuli, providing insights into gene expression, regulation, and protein binding.
