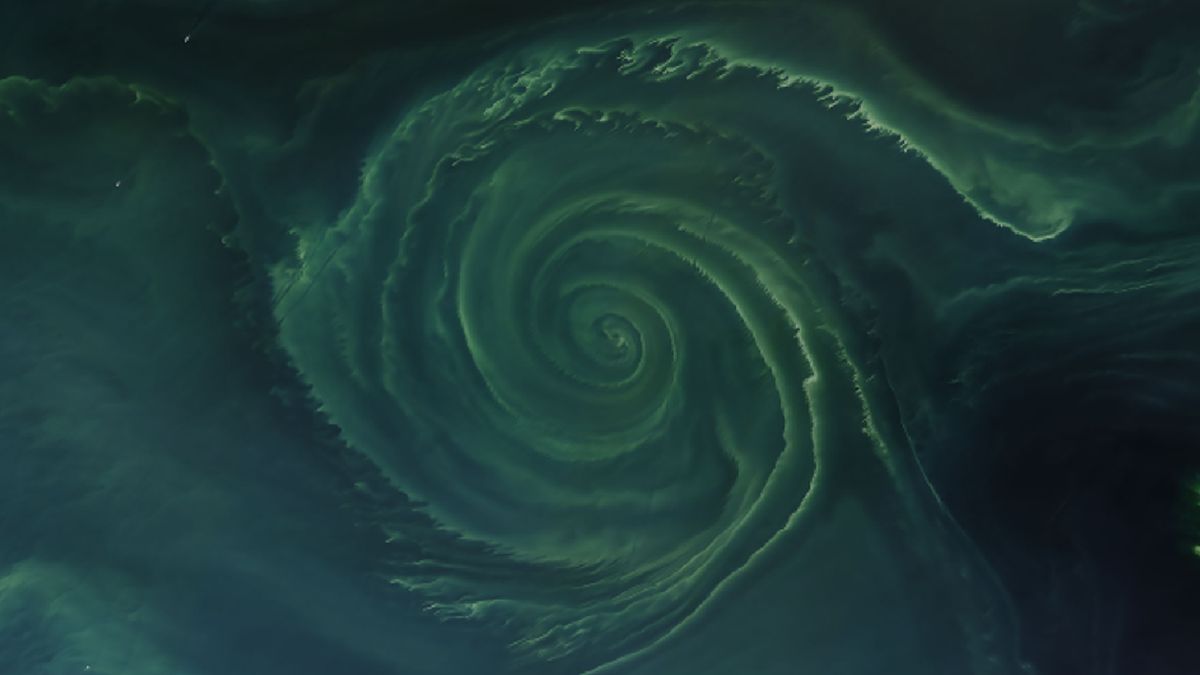
"Ethereal Algal Vortex Blooms in Baltic 'Dead Zone' Seen from Space"
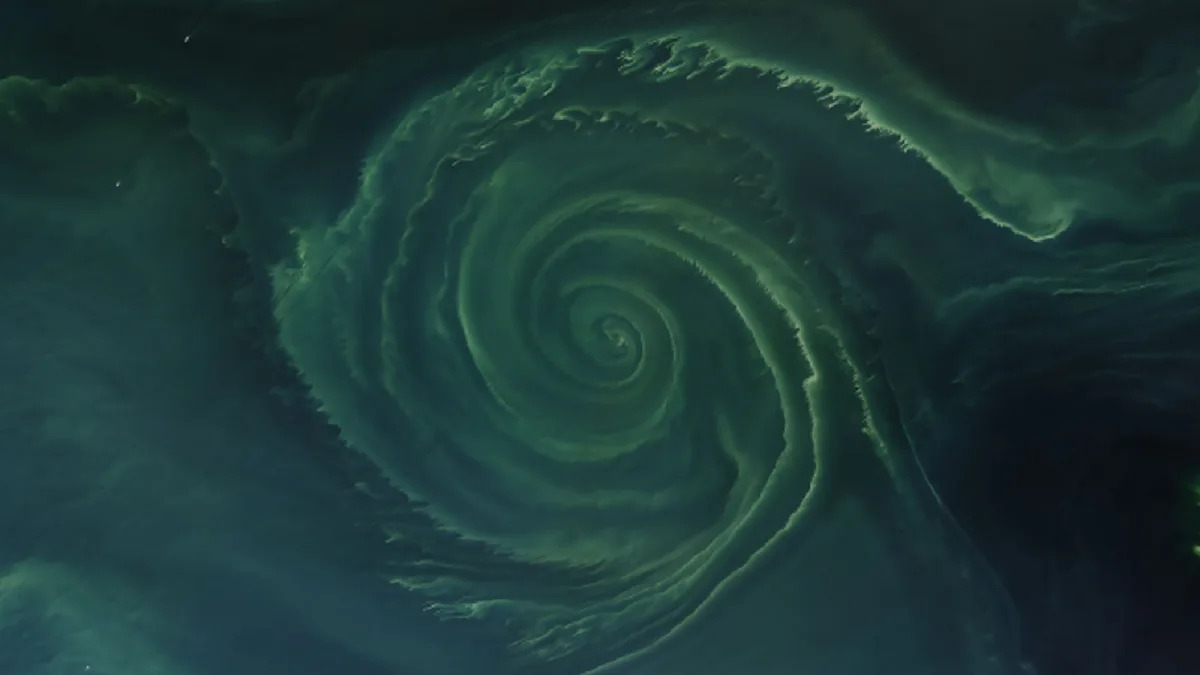
A striking image captured by NASA's Landsat 8 satellite in July 2018 shows a massive algal bloom in the Gulf of Finland, part of the Baltic Sea. The bloom, consisting mainly of cyanobacteria, formed a 15.5-mile-wide spiral and created a large "dead zone" due to decreased oxygen levels in the water. These blooms have increased in size and frequency due to nutrient run-off from human activities and rising sea temperatures, exacerbating the problem.


