Boosting Brain's Waste Disposal System Reduces Swelling After Injury
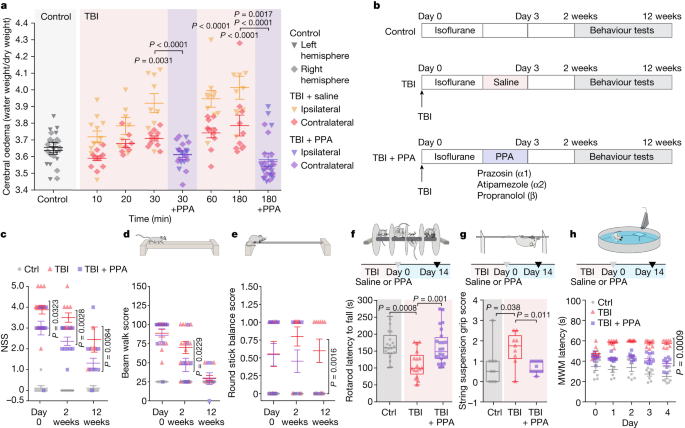
A study has found that enhancing glymphatic drainage, the brain's waste clearance system, can reduce post-traumatic cerebral edema, a major complication of traumatic brain injury. The researchers discovered that norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter involved in the body's stress response, plays a crucial role in regulating glymphatic function. By blocking the lymphatic vessels or inhibiting norepinephrine release, they observed an increase in brain edema. Conversely, stimulating norepinephrine release or enhancing glymphatic drainage through pharmacological interventions reduced cerebral edema. These findings suggest that targeting the glymphatic system and norepinephrine signaling could be a potential therapeutic strategy for minimizing brain edema following traumatic brain injury.
