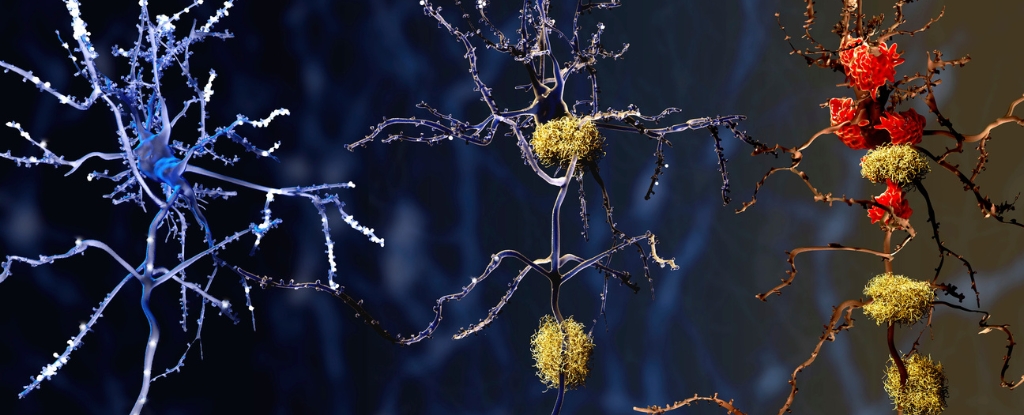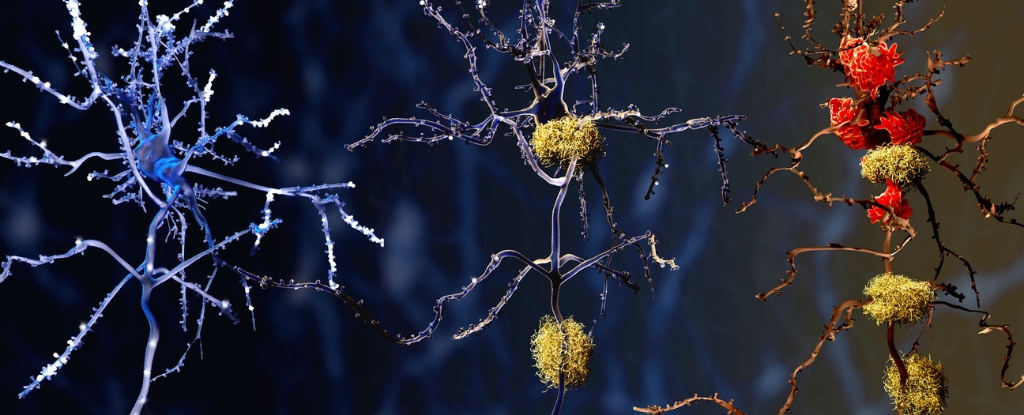
Unveiling a Promising Culprit in Alzheimer's Disease: Brain Autopsies Reveal New Insights
Brain autopsies have revealed that microglia, immune cells responsible for maintaining brain health, behave differently in individuals with Alzheimer's disease compared to those with healthy brains. Researchers found that microglia in Alzheimer's brains were more frequently in a pre-inflammatory state, producing inflammatory molecules that can damage brain cells and contribute to disease progression. The study identified new clusters of microglia with genes involved in inflammation and cell death, suggesting potential targets for new treatments. Understanding the role of microglia in Alzheimer's disease could lead to therapies that prevent or slow the progression of the disease.