"Magnetic Whirls: Unlocking the Potential for Next-Generation Computing and Data Transfer"
TL;DR Summary
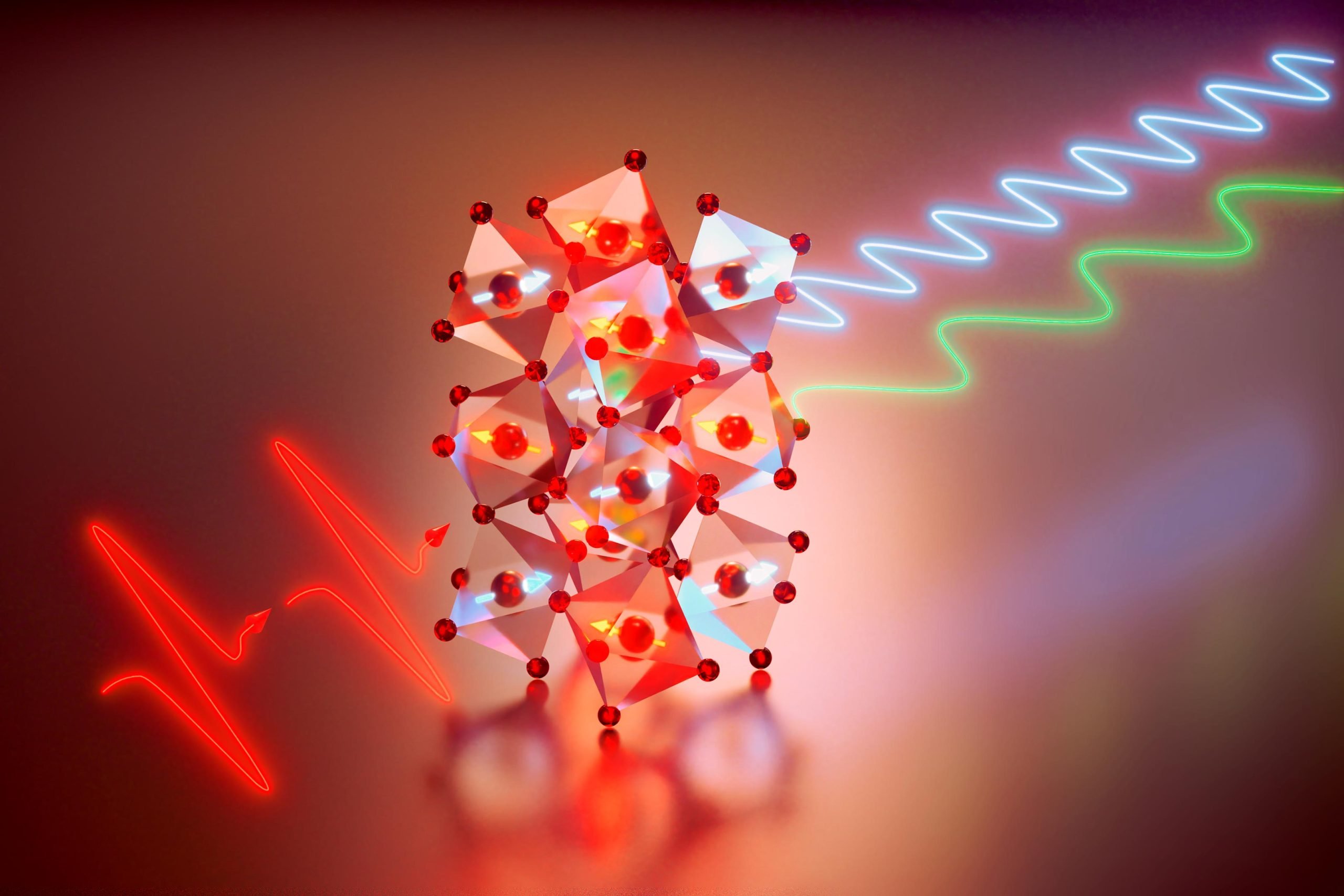
Researchers have made a significant advancement in magnonics, a field that explores the use of magnons, or ripples in magnetic fields, for computing technologies. By causing two distinct types of magnons to interact nonlinearly using terahertz laser technology, the study marks a crucial step towards faster and more stable computing devices. This research collaboration, involving institutions such as UCLA, MIT, and the University of Texas at Austin, aims to push the boundaries of nonequilibrium physics and nonlinear control in magnonics, potentially revolutionizing the future of computing.
Topics:science#computing-technologies#magnonics#nonlinear-phenomena#research-collaboration#technology#terahertz-laser
- Eclipsing Silicon: The Emergence of Magnon-Based Computing Technologies SciTechDaily
- Researchers achieve breakthrough in silicon-compatible magnetic whirls Phys.org
- Tiny 'Hurricane-like' magnetic swirls could hold key to next AI breakthrough — material found in rust could help power energy efficient, brain-like processors capable of running at hundreds of Gigahertz TechRadar
- Oxford-made magnetic whirls could transfer data at kilometers per second Interesting Engineering
- Exploring the Potential of Magnetic Whirls in Membrane Technology AZoQuantum
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
10
Time Saved
5 min
vs 6 min read
Condensed
92%
1,054 → 86 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on SciTechDaily